Introduction
The quality of health care and the initiatives taken to address various risk and safety issues in hospitals has become a subject of debate. Many countries and organizations are exploring various means to improve the quality of healthcare services.
“Accreditation is a status that is conferred on an organization that has been assessed as having met particular standards”. The two conditions for accreditation are an explicit definition of quality (i.e., standards) and an independent review process aimed at identifying the level of congruence between practices and quality standards. This article simplifies the process of accreditation into concise and simplified ten steps.
Step 1: Deciding to Get Accredited
Accreditation is not a goal but a journey. Accreditation is a continuous process rather than a final destination.
Step 2: Assessing the Current Situation and Doing Background Research
What stage is your organization at with regard to implementing quality standards?
- Considering options – whether to go for accreditation now or later
- Reviewing standards and preparing for implementation
- Preparing materials for Accreditation/ Certification
- Already Accredited / Certified
- Assessed unsuccessfully, preparing for re-assessment
- Assessed unsuccessfully / Not prepared.
Acquiring basic knowledge from available material
Collecting and assimilating knowledge regarding accreditation can be important in the initial stages. The required knowledge is made available in the form of books and guides, which include NABH Standards ( can be downloaded from the NABH website), NABH Guidebooks for ECO ( can be bought from NABH) and Resources on accreditation ( AIOS ARC booklet on Accreditation of Eye Centres - Edited by Dr Nirmal Fredrick) and articles published in the various journals. The NABH standards and guidelines book are strategically divided into ten chapters, focusing on Patient Safety and Quality to reduce the risk for patients and give an indication of Standards of care and provide professional satisfaction for Ophthalmologists and allied medical professionals.
Forming a good team to lead and implement the standards
A core team consisting of a quality coordinator is to be formed, which is to comprise different departmental teams, including Quality Committee, Safety Committee, CPR Committee, Clinical Audit Committee, Infection Control Committee and Pharmacy Committee.
Step 3: Conducting Gap Analysis and Build Action Plan
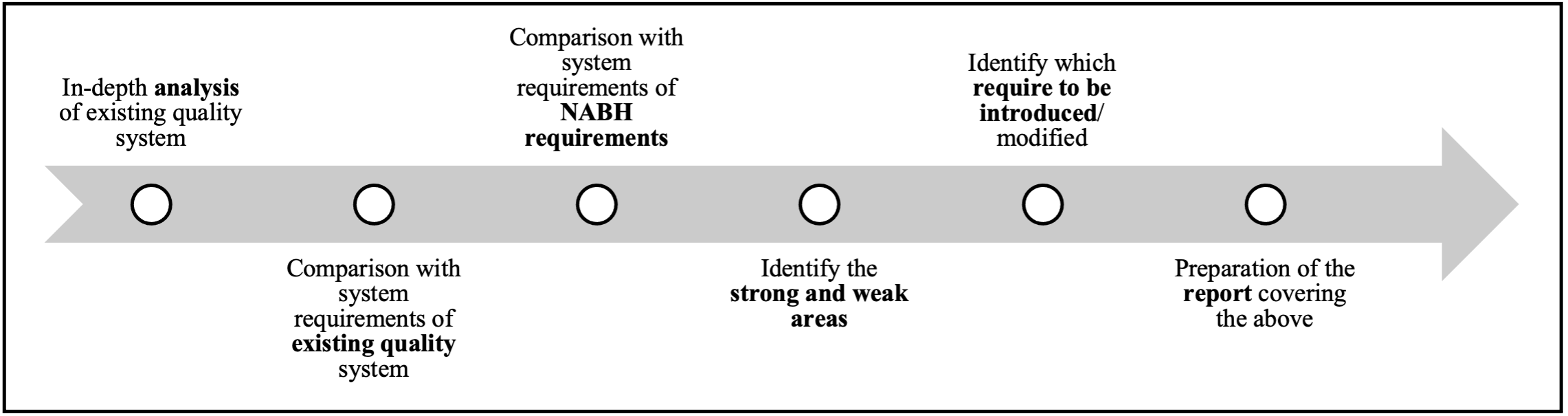
Gap Analysis and Follow up
1. Review the activities and task within the five domains every 3months.
2. Activities/ tasks assessed as being: Fully Met/ Partially Met/Not Met
Discuss and plan on how to reach the Fully met requirements
Step 4: Standards Awareness Training
Training the management and staff is an important step in the implementation of accreditation requirements. Training of all faculty, including ophthalmologists, optometrists, nursing staff, pharmacists, technicians and all staff, is an essential component of the process. This ensures that everyone is aware of what is expected from them and their role in the process of accreditation. Training can be done in several ways. Various methodologies include didactic lectures, workshops, and practical skill assessment programs, which can be in multiple sessions to systematically train and qualify the health personnel to work up to the standards of accreditation. It is important to take feedback and also audit the outcomes of the training by an effective pretest and post-test questionnaire.
Step 5: Emphasizing Documentation
Documentation is an important aspect and a cornerstone in the process of accreditation. Documentation takes multiple forms, as depicted in the quality pyramid (Fig 2). Each sub-component has comprehensive information regarding various guidelines in patient care. Of these, the Apex manual, Quality and infection control manuals form the core of documentation. For a Single speciality eye centre, they can be broadly divided into four categories (Fig 3)
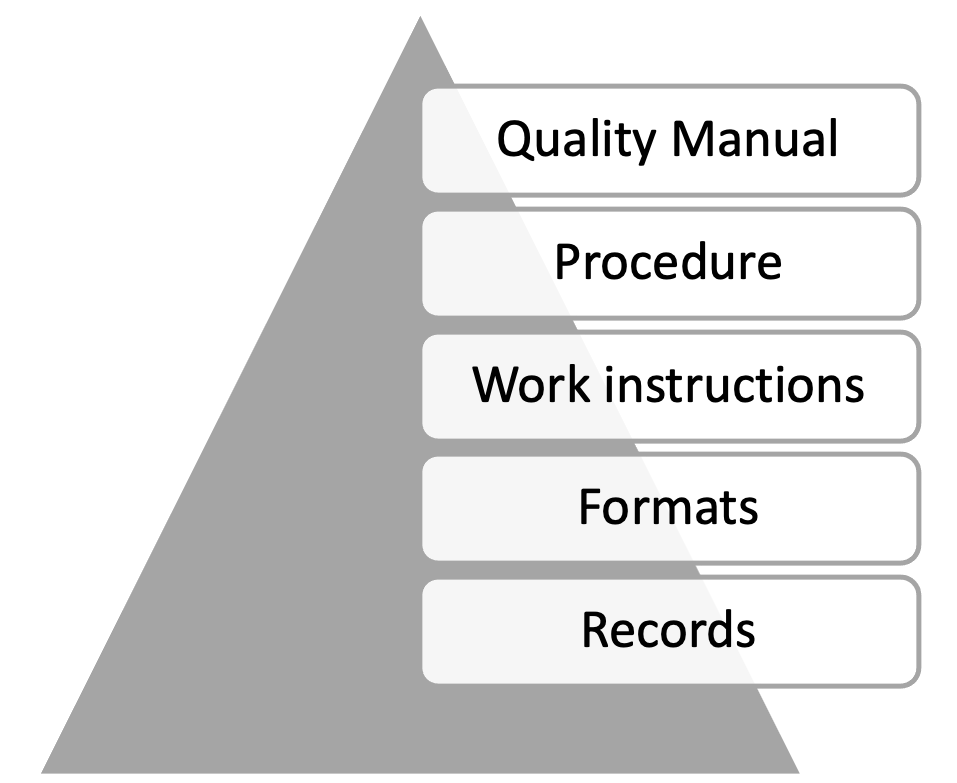
Fig 2: Quality Pyramid for Accreditation
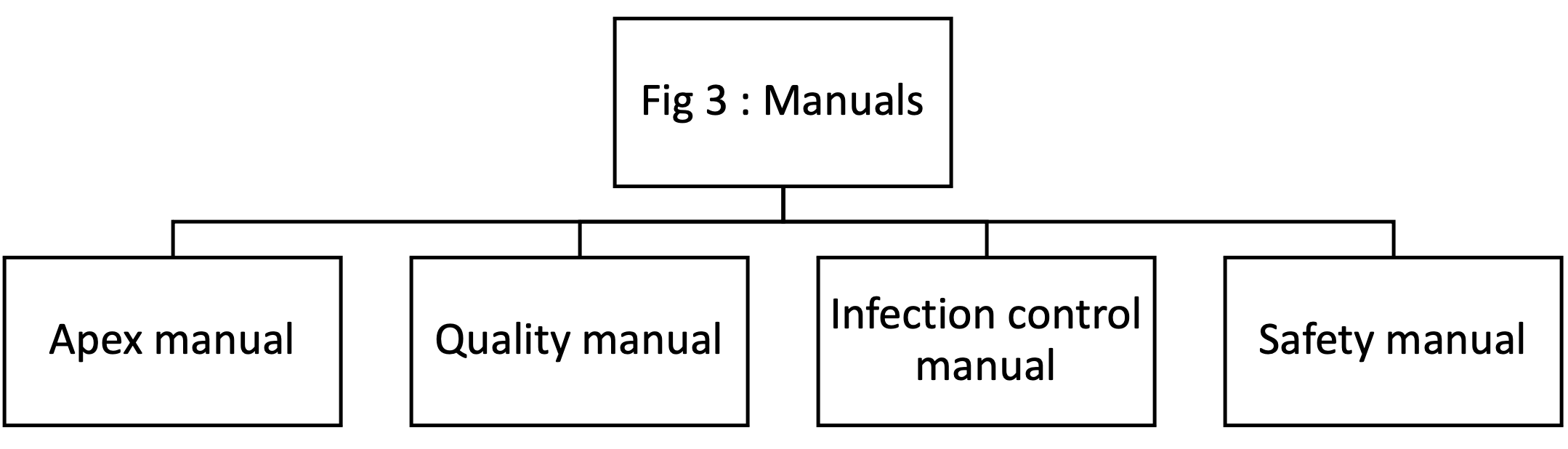
Manuals and SOPs addressing the ten chapters and some of the important processes in the hospital have to be written by the staff and administrators. Essentials the documentation should reflect the care provided in the hospital – DO WHAT YOU WRITE: WRITE WHAT YOU DO.
Step 6: Mentoring and Coaching for Implementation
Domains to be covered in training healthcare personnel are classified into patient and organizational standards. They include many subcomponents (Fig 4), which have to be dealt with in detail to all healthcare personnel for efficient knowledge transfer.
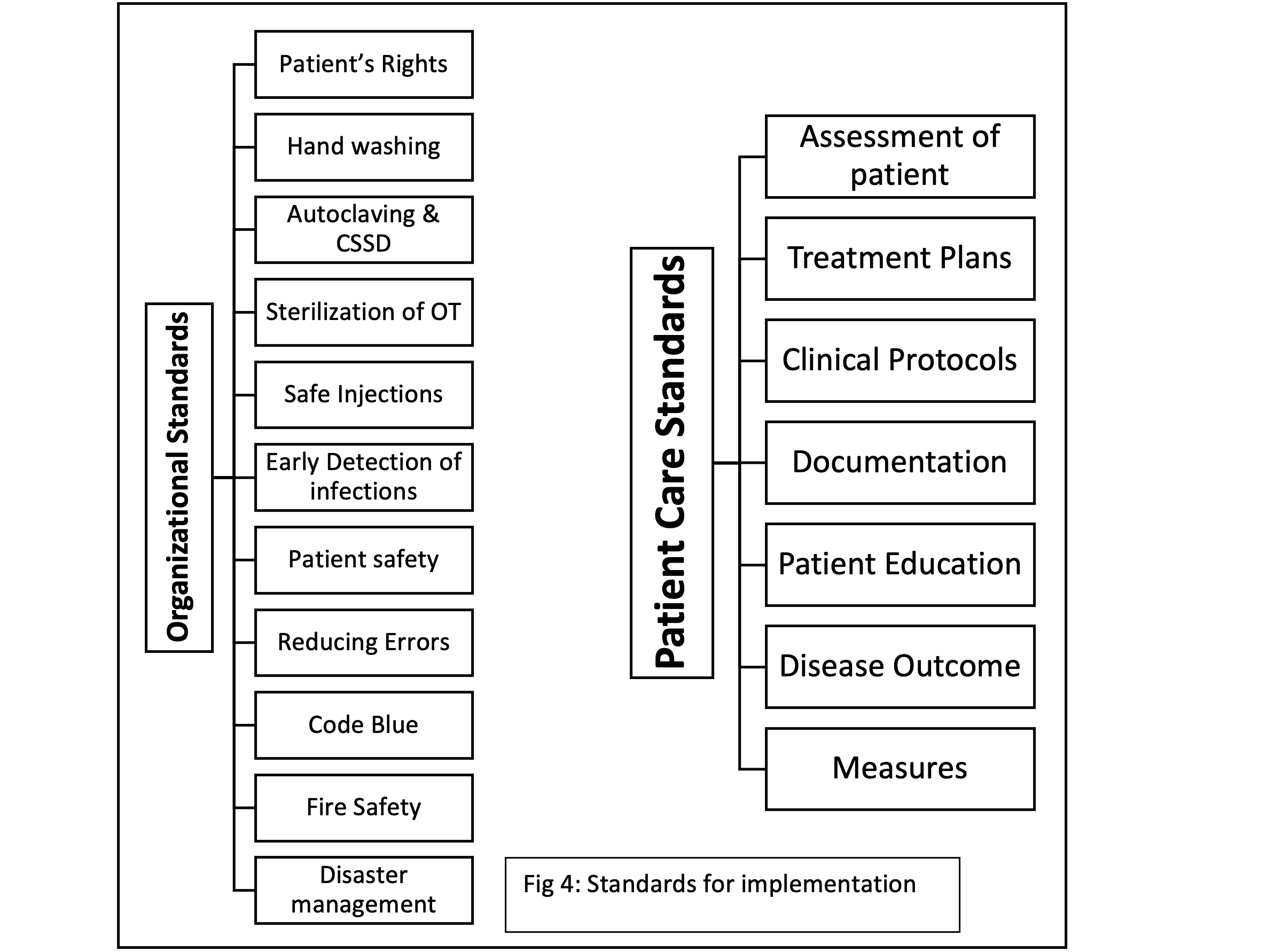
Following implementation, it is of high importance to repeatedly assess the practice patterns among the different strata of healthcare workers in the form of internal audits and identify the lacunae in successful implementation. New and simplified methods have to be adopted and changes made in order to overcome these obstacles and to ensure smooth implementation of the specified standards.
Step 7: Implementating of New System Requirements
The quality has to be evaluated objectively at three different levels, namely service level, quality control and customer satisfaction, as shown in the table below.
|
S. No |
Quality Objectives |
Performance Indicators |
Responsibility |
Measurement Criteria |
|
|
Criteria |
Frequency |
||||
|
1 |
Service Level |
Staff availability |
Hod, HR Manager |
Duty Roster/ Attendance record |
Monthly |
|
Staff skills |
Hod, Training coordinator |
Staff job description and staff resumes |
Half yearly |
||
|
Investigation time |
HOD, Imaging Services |
Imaging department patient registration record imaging department procedure record |
Monthly |
||
|
Coordination between all staff |
Quality coordinator or administrator |
Patient Feedback Form |
Monthly |
||
|
2 |
Quality Control |
Internal quality control process |
Quality coordinator or administrator |
Quality Control Records |
Monthly |
|
External quality control |
Quality coordinator or senior administrator or top management |
Quality Control Records |
Half yearly |
||
|
3 |
Customer Satisfaction |
Courtesy level |
Chairperson, Quality Committee PRO |
Patient Feedback Form |
Monthly |
|
wait time and convenient reports collection |
Quality team and PRO team |
Patient Feedback Form |
Monthly |
Step 8: Audit & Continuous Quality Improvement
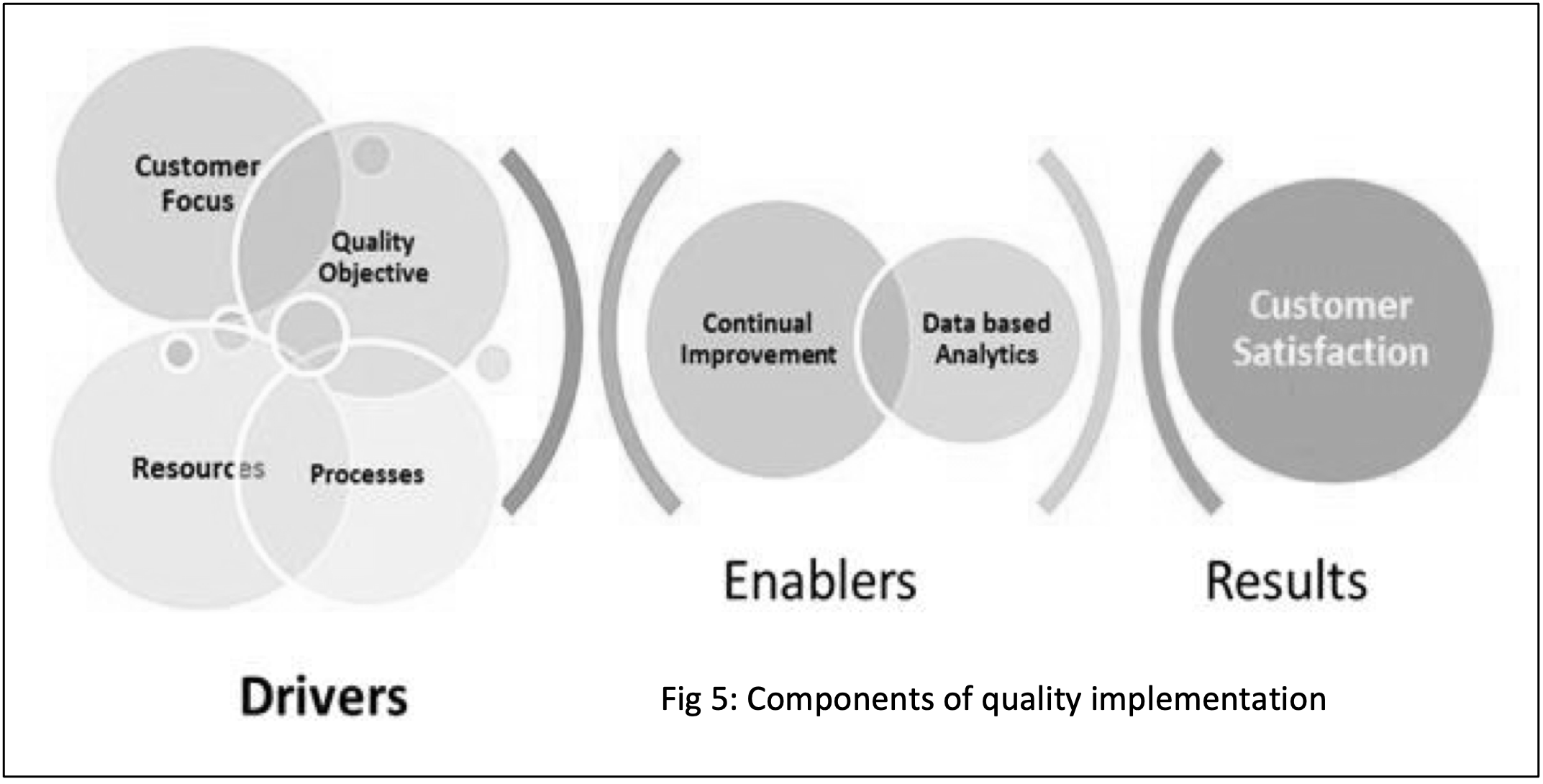
Systematic implementation of the process at two different levels, namely the “drivers”, “enablers”, can ensure a fruitful outcome in the form of customer satisfaction (Fig 5)
Step 9: Challenges in The Process
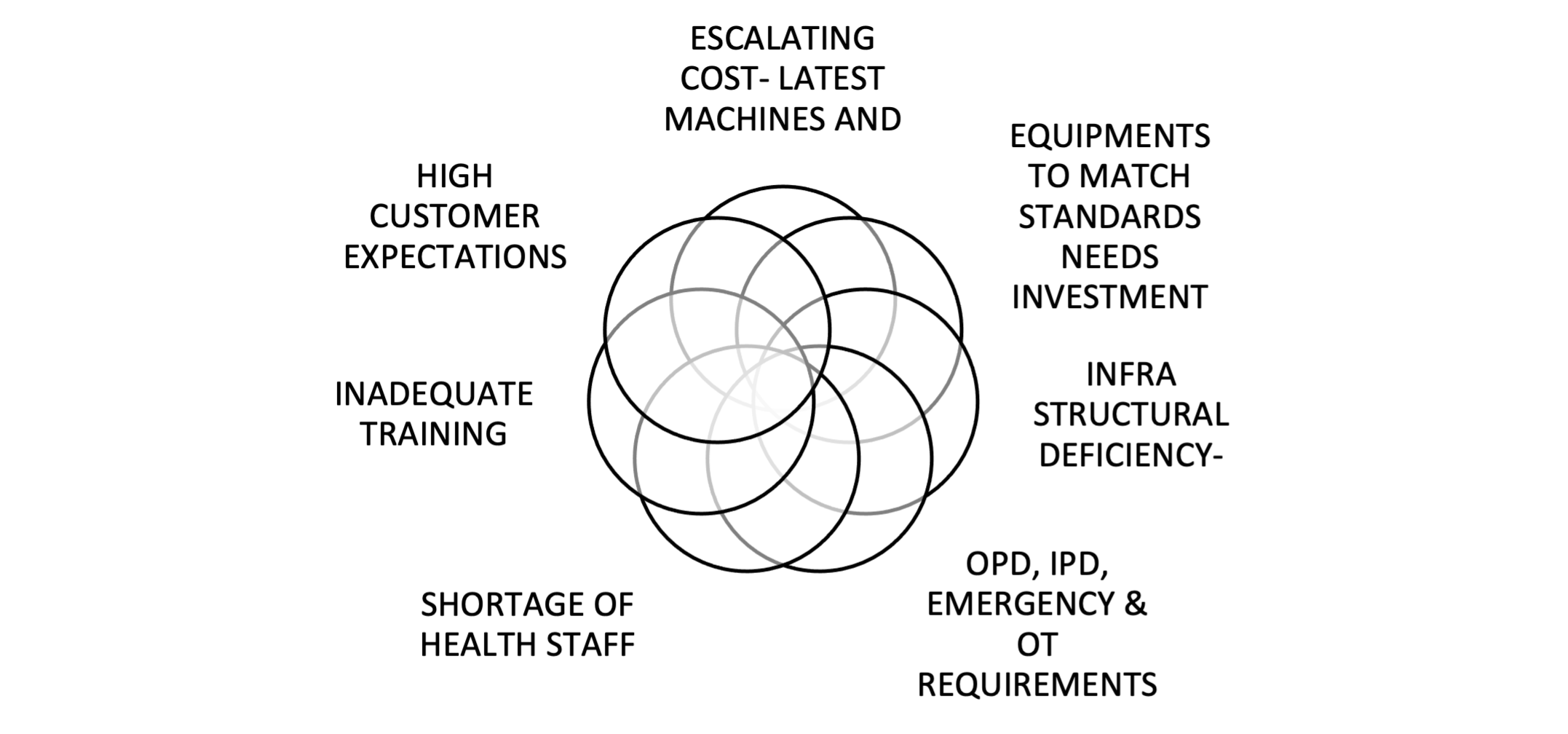
In the journey of implementation, several hurdles are to be anticipated and appropriately handled.
Step 10: Applying & Being Ready for Assessment
After implementing the above steps and after a round of internal audits, if we are satisfied that the hospital is ready for the third-party assessment, an online application is made. All these details and resource materials are available at www.nabh.co.in. It is important to go through all the resource materials and have thorough discussions with those who have implemented the standards and experts who can facilitate the understanding and help in implementation.
Quality of care or services has become an essential part of the management and evaluation of health care. It has become a prime consideration to ensure patient satisfaction. Therefore, Accreditation standards promote continual training and development programs for doctors and hospital staff, thereby helping to improve service quality and patient satisfaction.
References
- Nirmal Fredrick T, Nirmal S Accreditation of Eye Hospitals – A Review. DJO 2014;25:118-124
- www.who.int/hrh/documents/en/quality_accreditation.pdf. Quality and accreditation in health care services A GLOBAL REVIEW. Evidence and Information for Policy, Department of Health Service Provision (OSD) World Health Organization, 1211 Geneva 27, Switzerland. 2003.
- Kimberley A, Galt K A: Foundation in Patient Safety for Health Professionals. Jones & Bartlett Publishers, LLC, 2011.
- nabh.co/Images/PDF/nabh_gib_hos.pdf:National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers General Information Brochure, 2013.
- nabh.co/images/pdf/all-gib.pdf: National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Guidebook to NABH Standards 2012.
- Myers S A. Patient Safety and Hospital accreditation A model for ensuring success. Springer Publishing Company, LLC, New York, 2012


