Oculoplasty Instruments
Oculoplasty deals with the aesthetic part of ophthalmology. Precision is the key in Oculoplasty as the outcomes depend on it. Good precision can be achieved with good knowledge of the instruments used in oculoplasty and when to use them. This article would give a brief idea on basic instruments used.
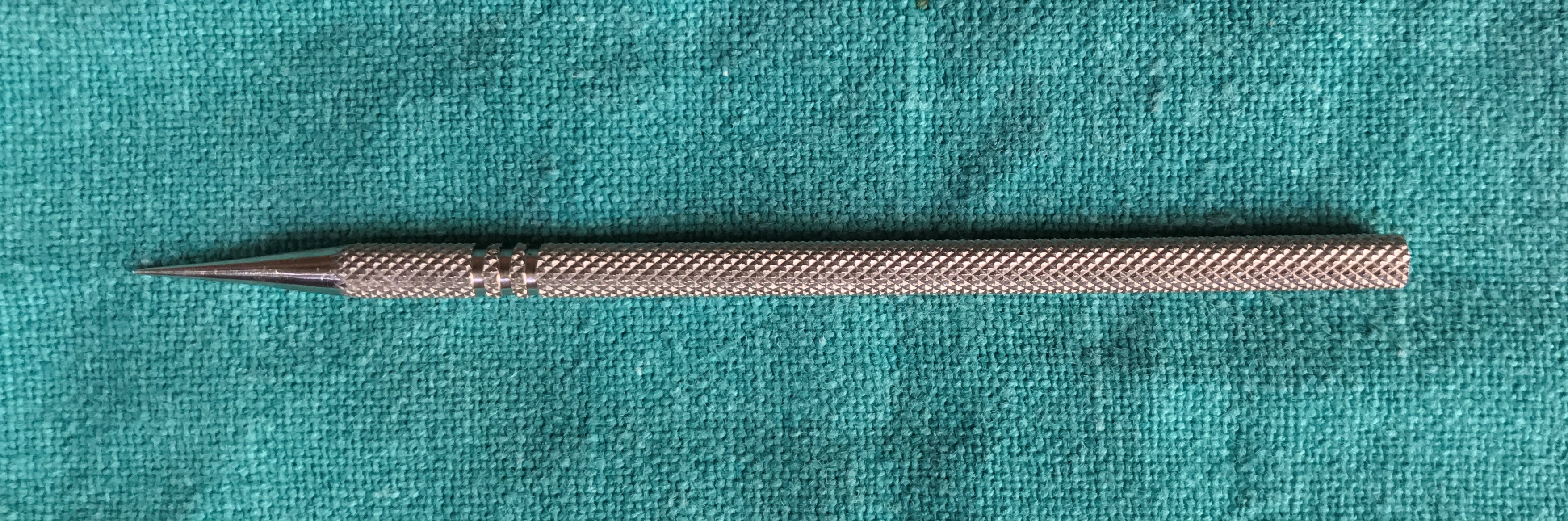
- Nettleship Punctum Dilator
- It is the instrument with very fine blunt tip, with a tapering end
- Uses
- Dilation of puncta during diagnostic and therapeutic probing
- Before syringing in small puncta,
- Diagnosing punctal stenosis,
- Canalicular repair with monoka stent,
- Silicone tube intubation
- Dilation of puncta during diagnostic and therapeutic probing

- Castroviejo Lacrimal Dilator
- It is the instrument with Double-ended with fine and medium taper end.
- Uses
- Dilation of puncta during diagnostic and therapeutic probing
- Before syringing in small puncta,
- Diagnosing punctal stenosis,
- Canalicular repair with monoka stent,
- Dilation of puncta during diagnostic and therapeutic probing
- Thudicum’s Nasal Speculum
- It is a thin instrument with flanges, once the speculum is introduced it retracts the lateral wall of the nose and gives a good view of the nasal cavity. It is available in different sizes.
- Uses
- Used for nasal cavity examination
- The nasal speculum is used to widen the nostril before packing the nostril with roller gauze
- It can be used to identify the probe in NLD probing
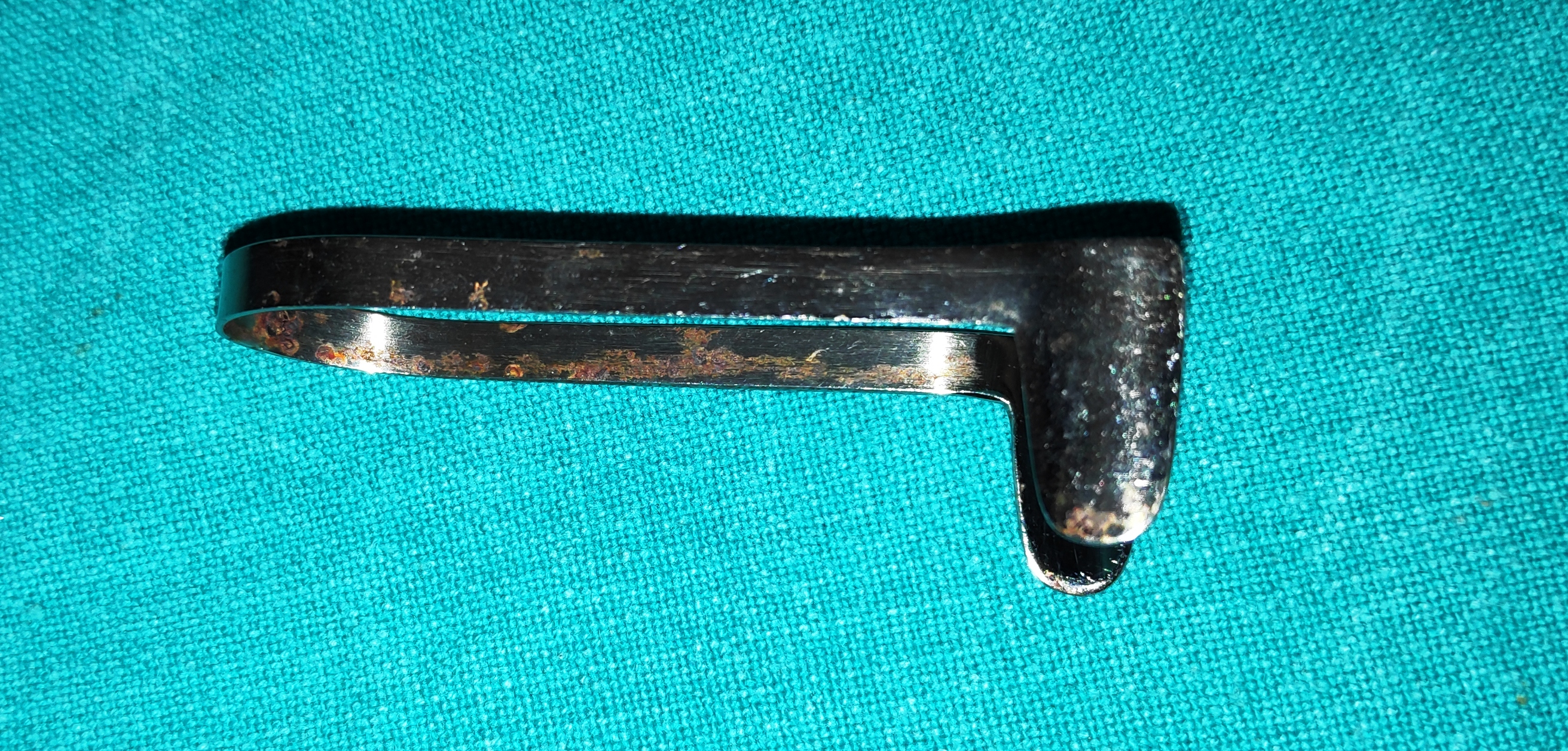

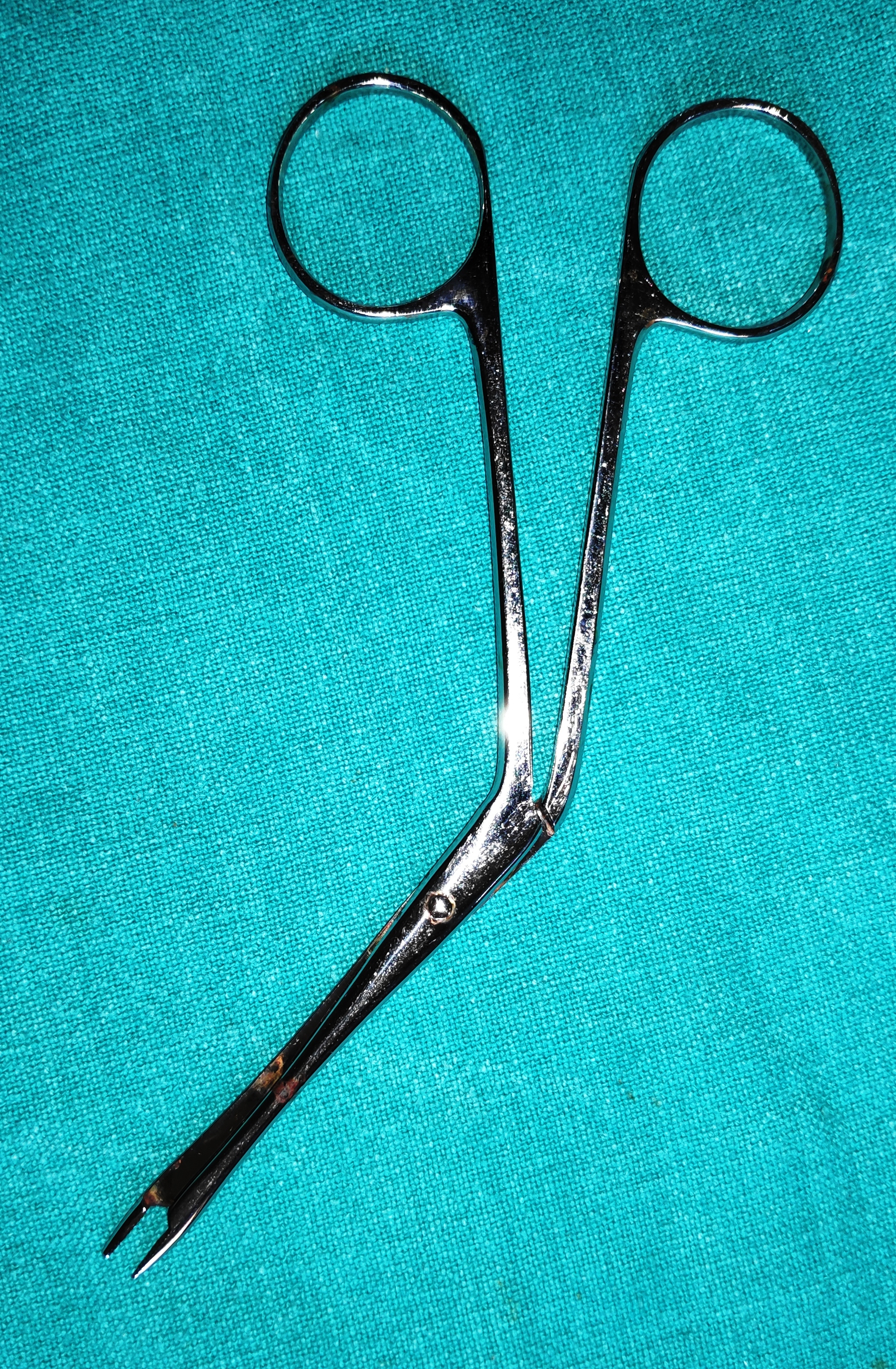
- Tilley’s Nasal Packing Forceps
- It is the long slender instrument with ring handle, and occult lap joint.
- Uses
- To pack the nostril with roller gauze soaked in xylometazoline solution.
- Tilley’s forceps can also be used during endoscopic nasal DCR to remove the remnant nasal mucosa and lacrimal sac tissue.
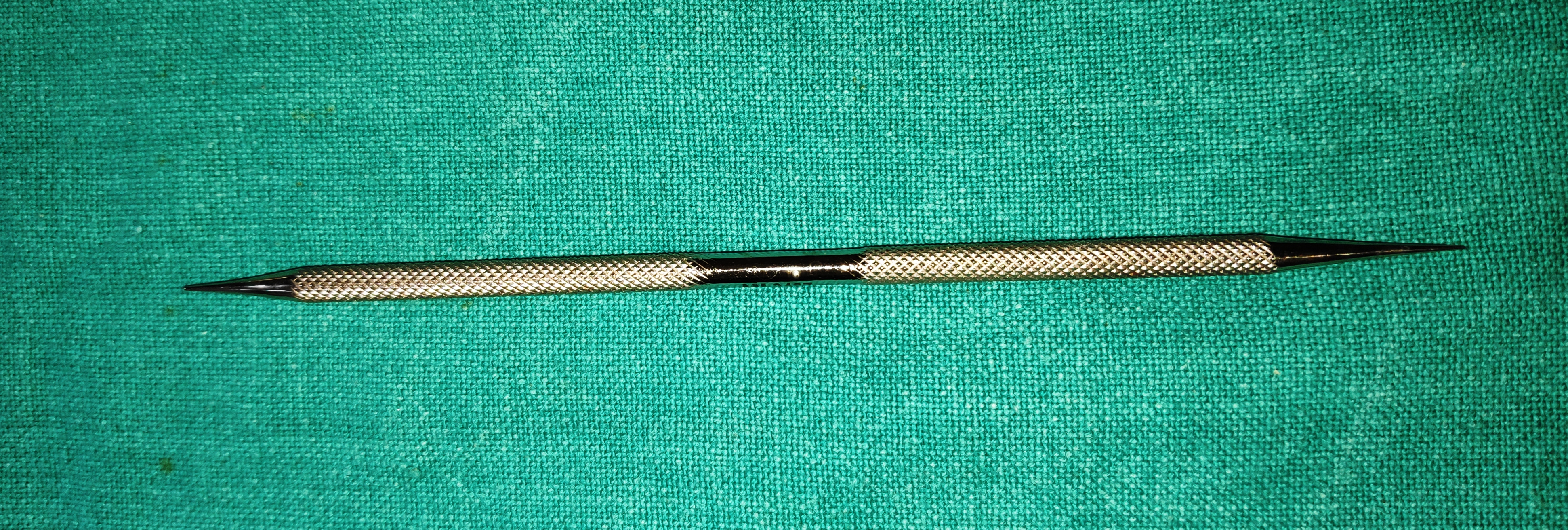
- Bowman’s Probes
- It is the wire-like instrument with marking on the hub depicting the diameter of the probe, more the gauge from 0000-4, more the diameter of the probe. (Bowman’s—#0000 = 0.7 mm, #000 = 0.8 mm, #00 = 0.9 mm, #0 = 1, #1 = 1.1 mm diameters)
- Uses
- Diagnostic probing (canalicular palpation)- To judge whether there is a soft or hard stop in patients with doubtful ROPLAS
- Therapeutic probing (CNLDO)-Probing and syringing in a child past sac massaging age
- Tenting of lacrimal sac during ext DCR
- Confirming the canalicular opening in cases of external and endonasal DCR
- Locating the distal end of cut canaliculi in cases of tr canalicular laceration

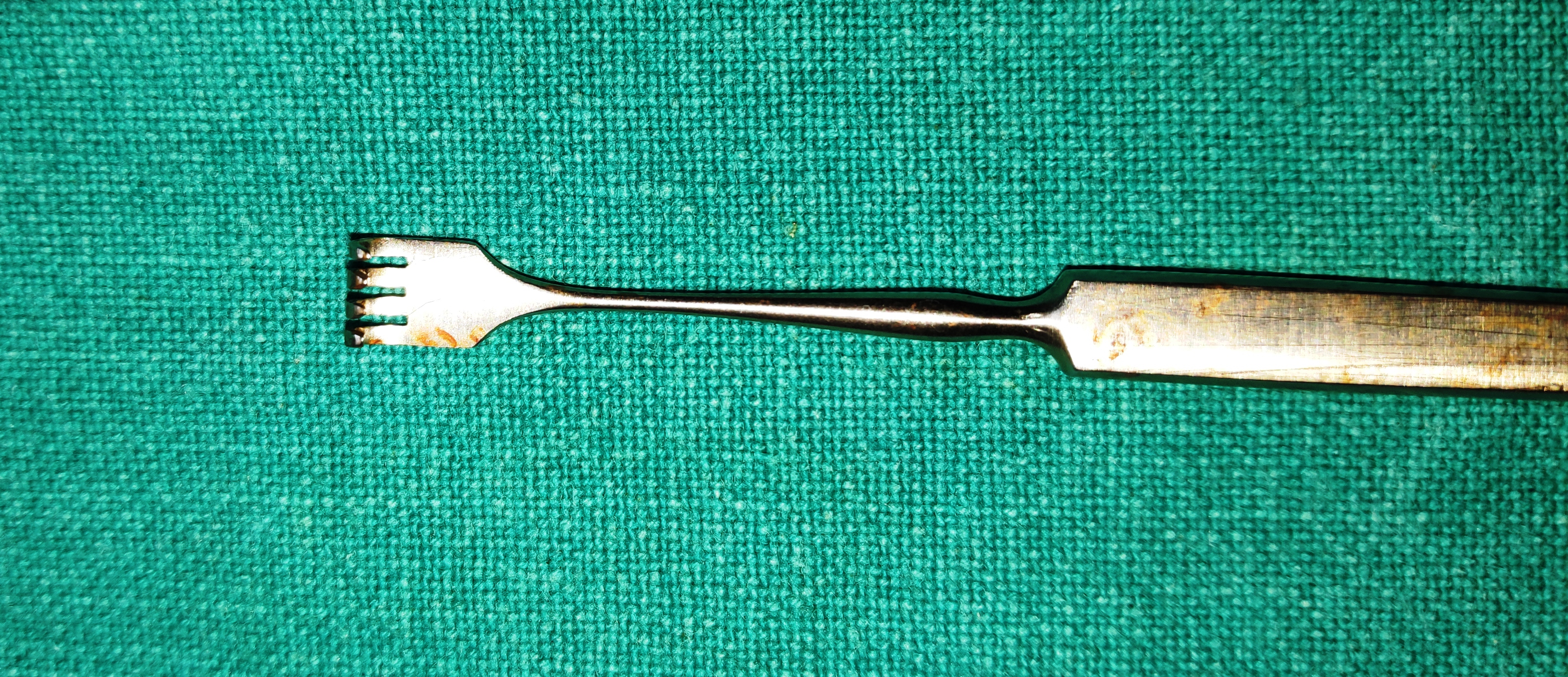
- Knapp’s or Rollet “Cat’s Paw” Retractor
- It is the Cat’s paw-shaped instrument with blunt tips and 4-5 prongs. It is part of the retractor family. It is atraumatic blunt with excellent retraction capabilities, it keeps the skin soft tissues etc away from the surgical field.
- Uses
- After the skin incision and the spreading and splitting of orbicularis oculi muscle, the wound margins are retracted with Cat’s paw retractor.
- To retract the tissues in general during oculoplastic procedures
- It can provide temporary compression to the bleeders
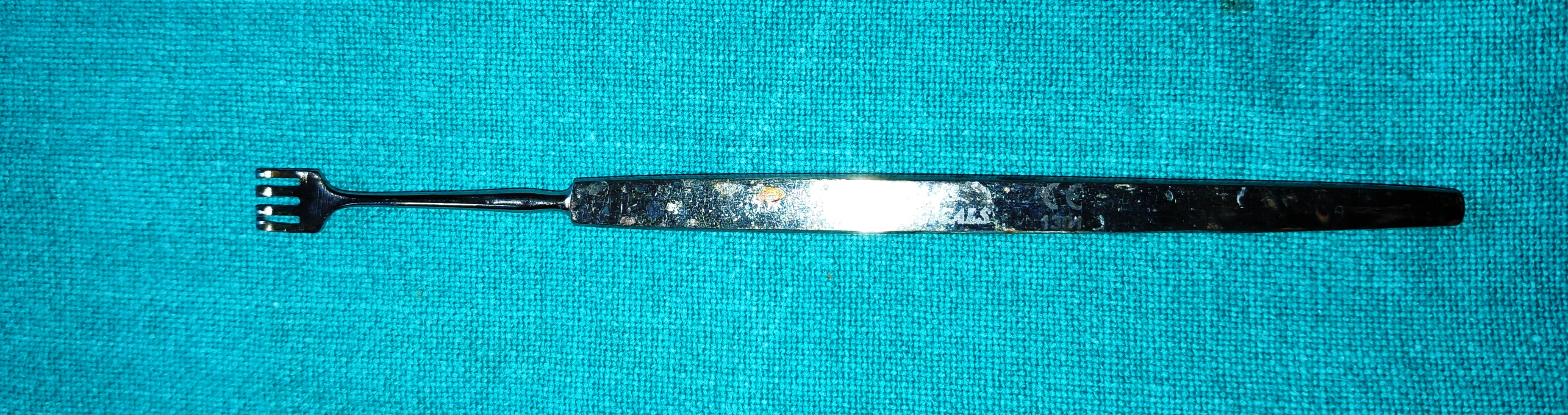

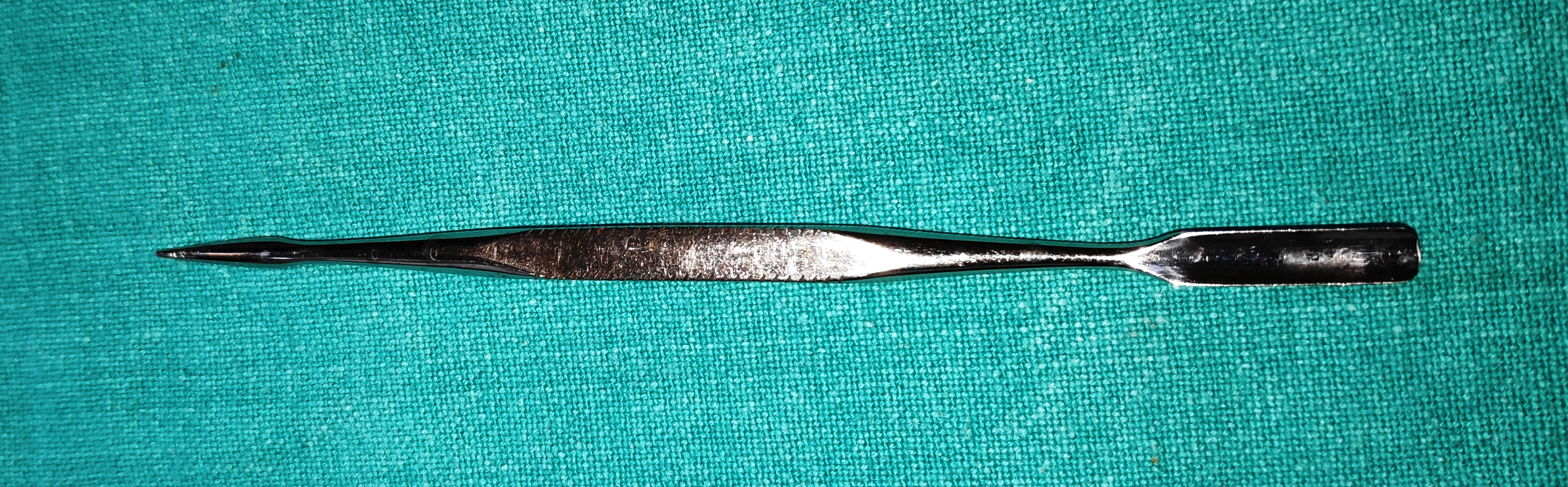
- Freer’s Double-Ended Periosteum Elevator
- It is the long slender instrument which tapers into double end sharp and blunt blades. The sharp end provides the cutting capacity to the tool and the blunt end aids in lifting the periosteum from the bone.
- Uses
- To elevate the periosteum off the bone before performing osteotomy in sac surgeries, orbital fracture repair, orbitotomy and orbital decompression
- To initiate osteotomy in external DCR by breaking the innominate suture
- It is used to hold tissue away from the surgical site.
- It can be used for blunt dissection between the tumour and the orbital tissues
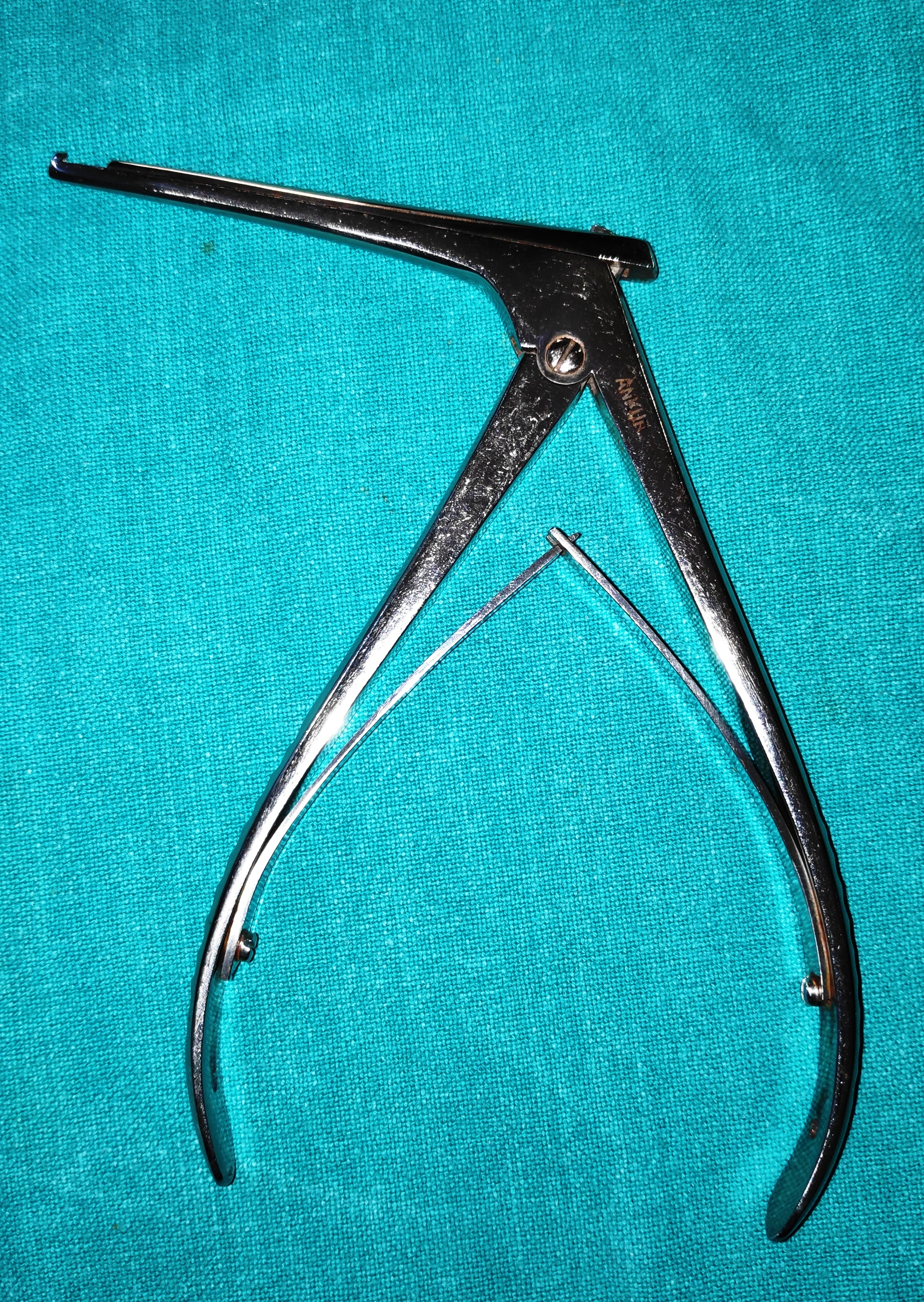
- Kerrison’s/ Bone Rongeur
- It is a stout and sturdy instrument, with 2 handles with spring joint. The tip of the instrument is used to punch the bone. It is available in different tips diameter ranges from 1.5 to 4 mm. According to the ostium size, the appropriate rongeur is used. The greater the size of the punch the larger the area it punches
- Uses
- The punch is used to remove the lacrimal fossa and the anterior lacrimal crest to expose the lateral nasal mucosa in DCR surgery.
- To remove the orbital bones during orbital decompression
- It is used to initiate the process of making ostium.
- It is less powerful compared to Rongeurs punch.
- Helpful during endonasal DCR
- Rongeurs are used to complete the ostium
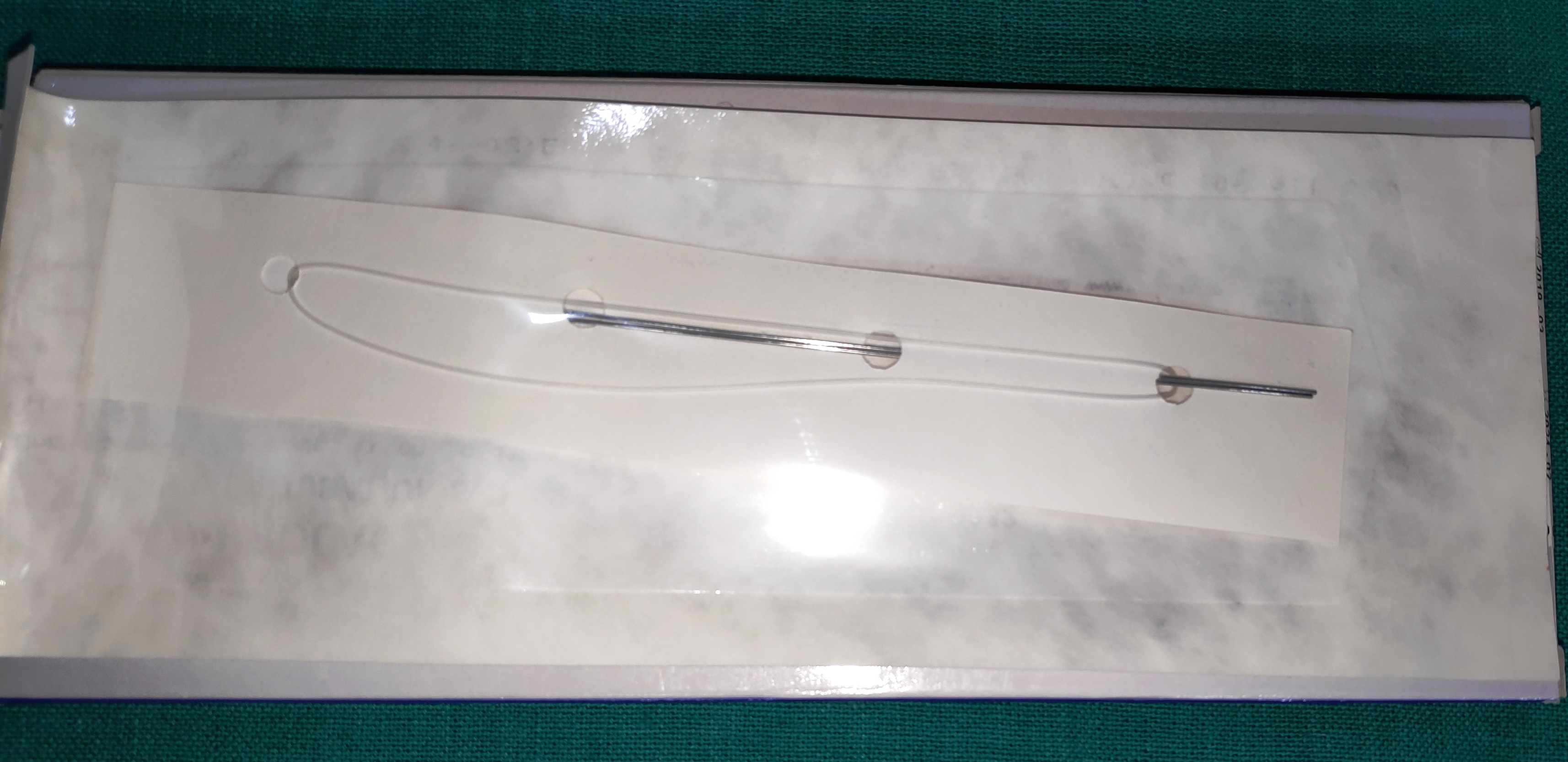
- Silicone Tube Intubation
- It is the thread-like silicone tube with two metal rod on either endfor introduction in the canaliculi
- It should be removed after 3 months.
- Uses
- It is used to maintain the patency of the tract created in DCR. (difficult DCR as in cases of traumatic NLDO, or if resistance is felt during passing a probe per op, failed DCR)
- The lacrimal passage is intubated with silicone tube bicanalicular stent after a difficult therapeutic probing or previously failed probing
- Functional NLDO (Controversial)
- Canalicular laceration repair especially bicanalicular lacerations.
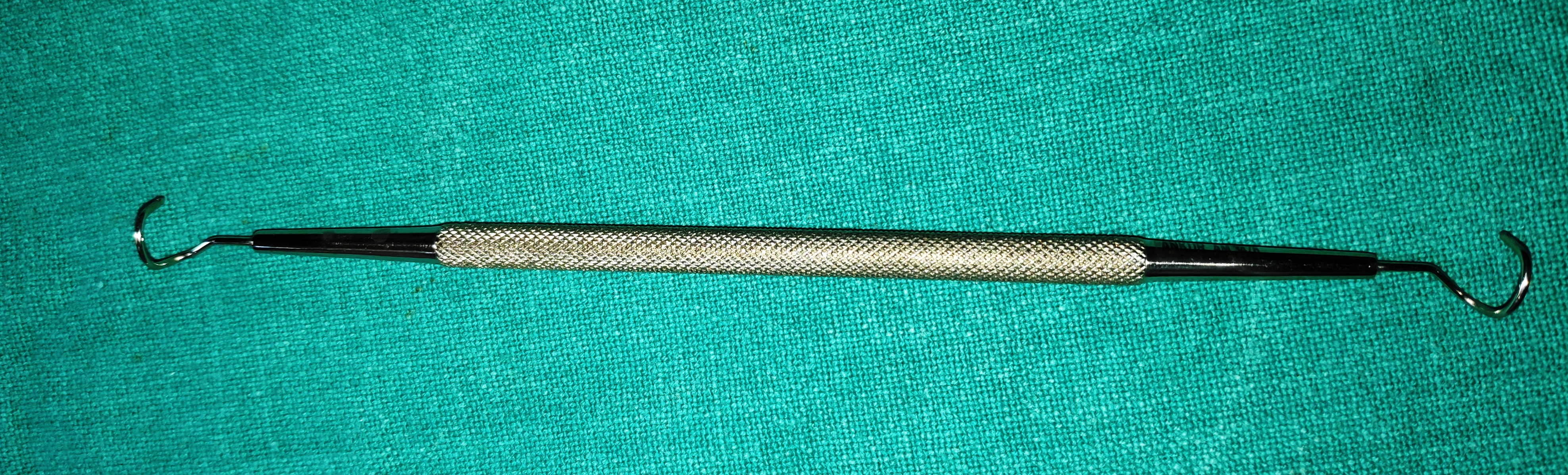
- Modified Worst’s Pigtail Lacrimal Probe with Eyelet
- It is the long instrument with the bent end in the shape of the pigtail, with eyelet. The end is round, atraumatic tips
- Uses
- Used in lacrimal canalicular lacerations to identify the medial cut end.
- To pass a silicone stent or nylon suture from the lacerated canaliculus and through the intact opposite punctum.

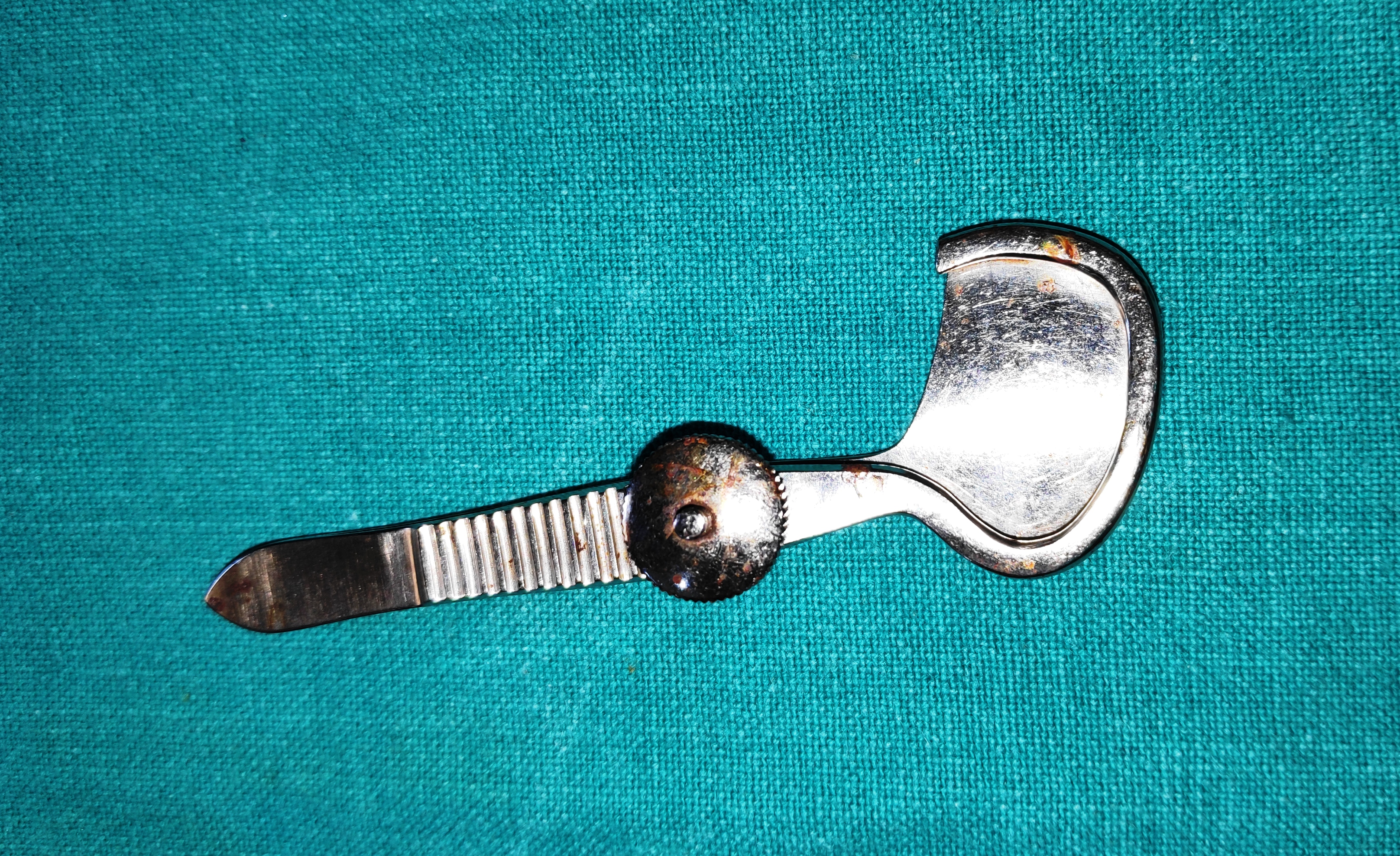
- Snellen Entropion Clamp
- It has “D” shaped plate with “U” shaped rim incorporated in it. The plate protects the eyeball during surgery and the rim provides proper compression for haemostasis. It has a screw joint in between both limbs.
- Uses
- It provides good protection to the globe along with proper haemostasis thus clear operative field.
- It provides proper traction to the lid while operating.
- Jaeger Eyelid Plate
- It is a flat, double-ended plate-like instrument with a convex and concave surface. The concave surface faces the globe for corneal protection.
- Uses
- It provides stability to the eyelid and tarsal plate while operating on the eyelid
- It would protect the cornea from various sutures or silicon rod.
- At times it can be used as a retractor.
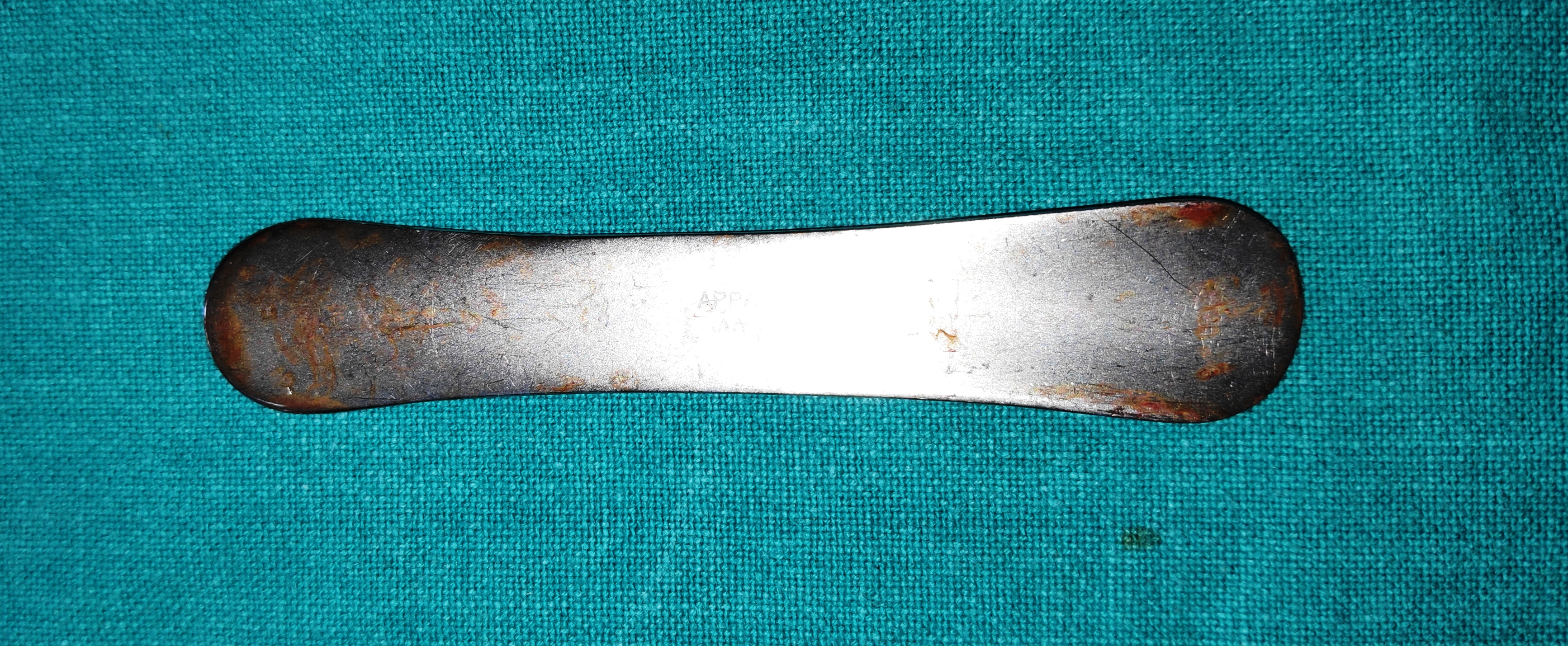
- Beer/ Barraquer Cilia Forceps
- It is a small forceps with smooth, stout round ends. The forceps have good grip for the eyelashes.
- Uses
- It is used to remove the eyelashes in trichiasis/distichiasis
- It can be used for suture removal also
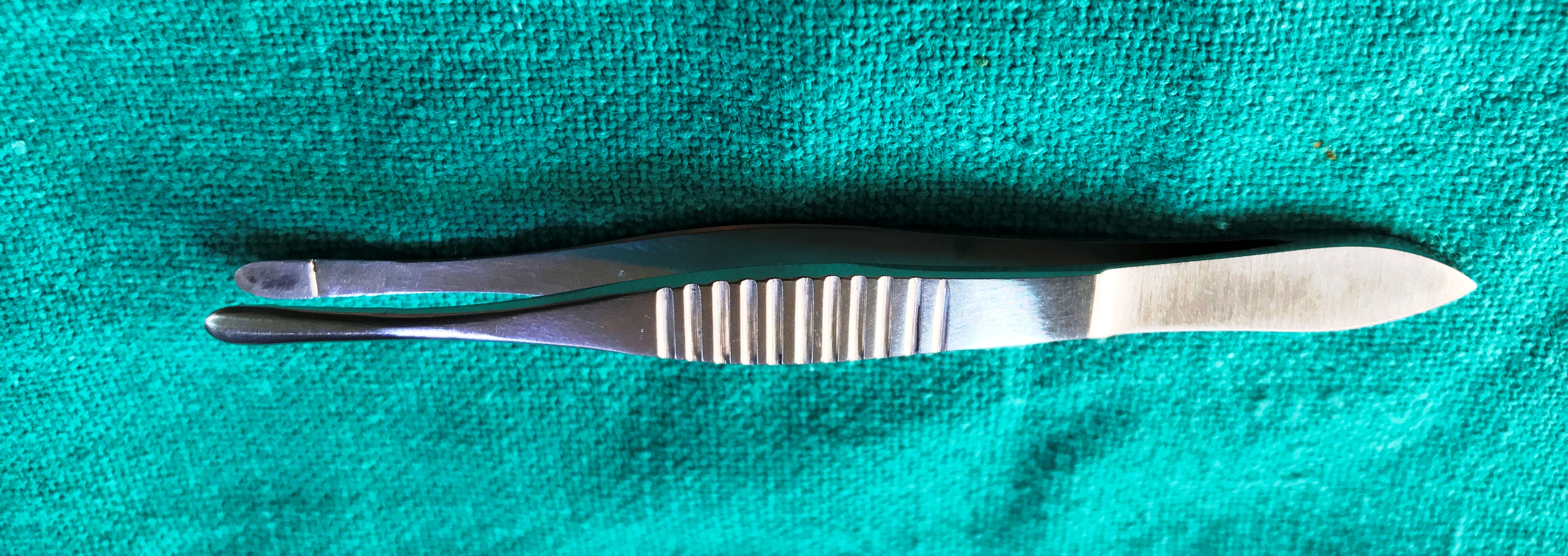
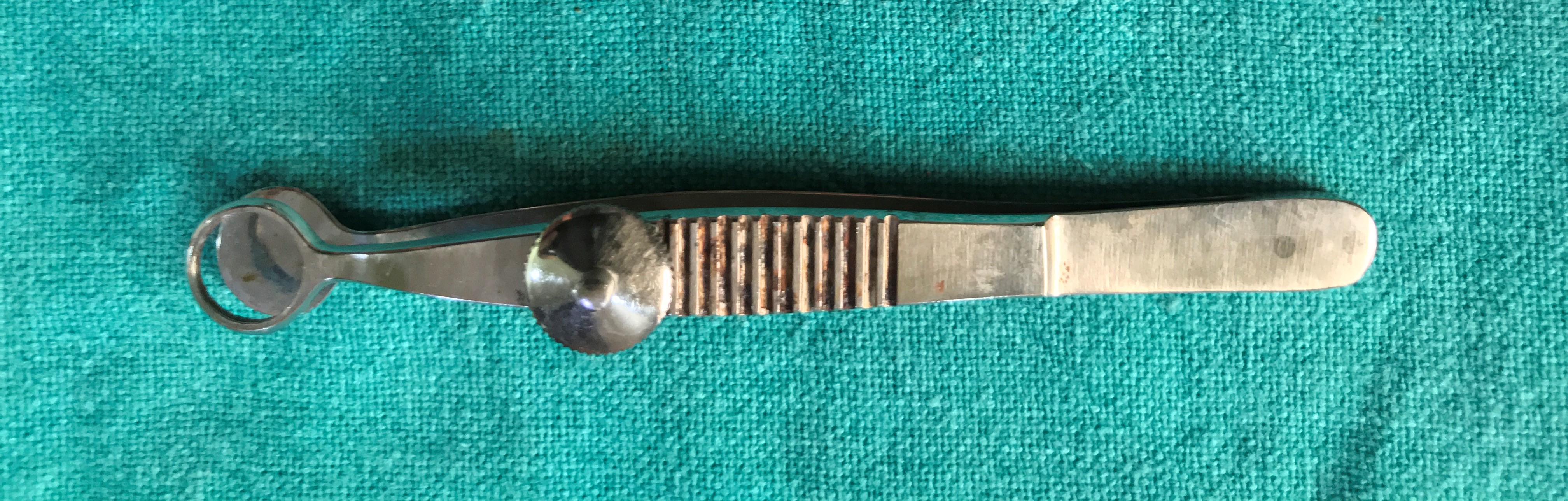
- Lambert Chalazion Clamp
- It is the clamp with a plate design on one arm and on the other, there is a ring shape clamp which provides the haemostasis and clear operating field. Both the arms are in place with the help of a screw knob.
- Uses
- It is used in incision and curettage of chalazion.
- It can be used for small eyelid mass excision or biopsy.

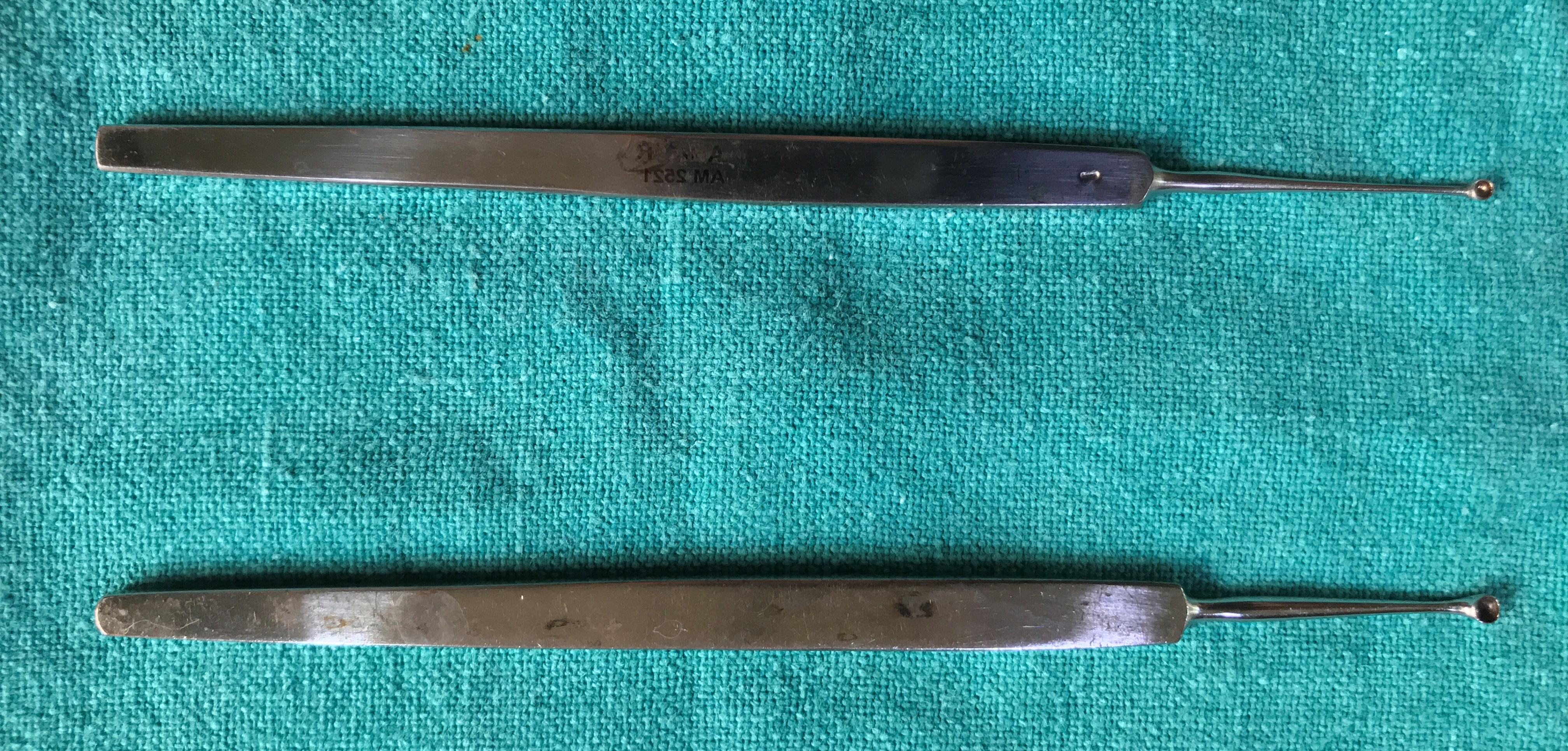
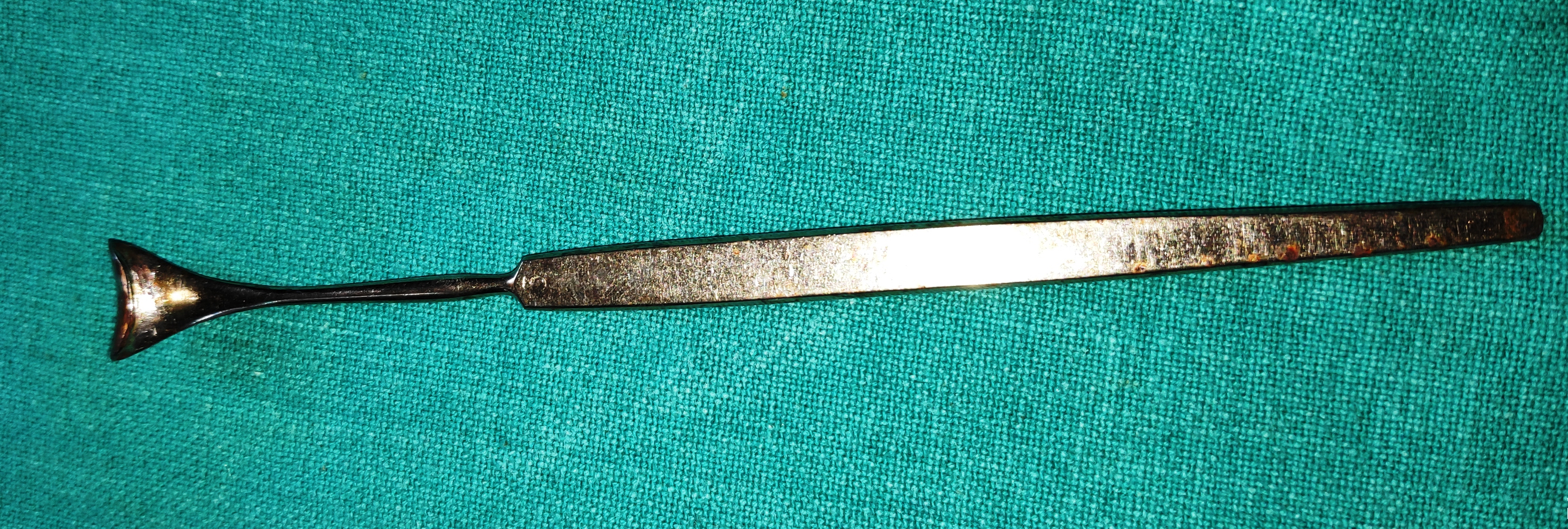
- Meyerhoefer Chalazion Curette
- It is the long slender instrument with the slender shaft and blunt round cup-shaped curette. It is available in various sizes
- Uses
- It is used to remove the cheesy material from the chalazion.
- It can be used for the foreign body from the tarsal plate.

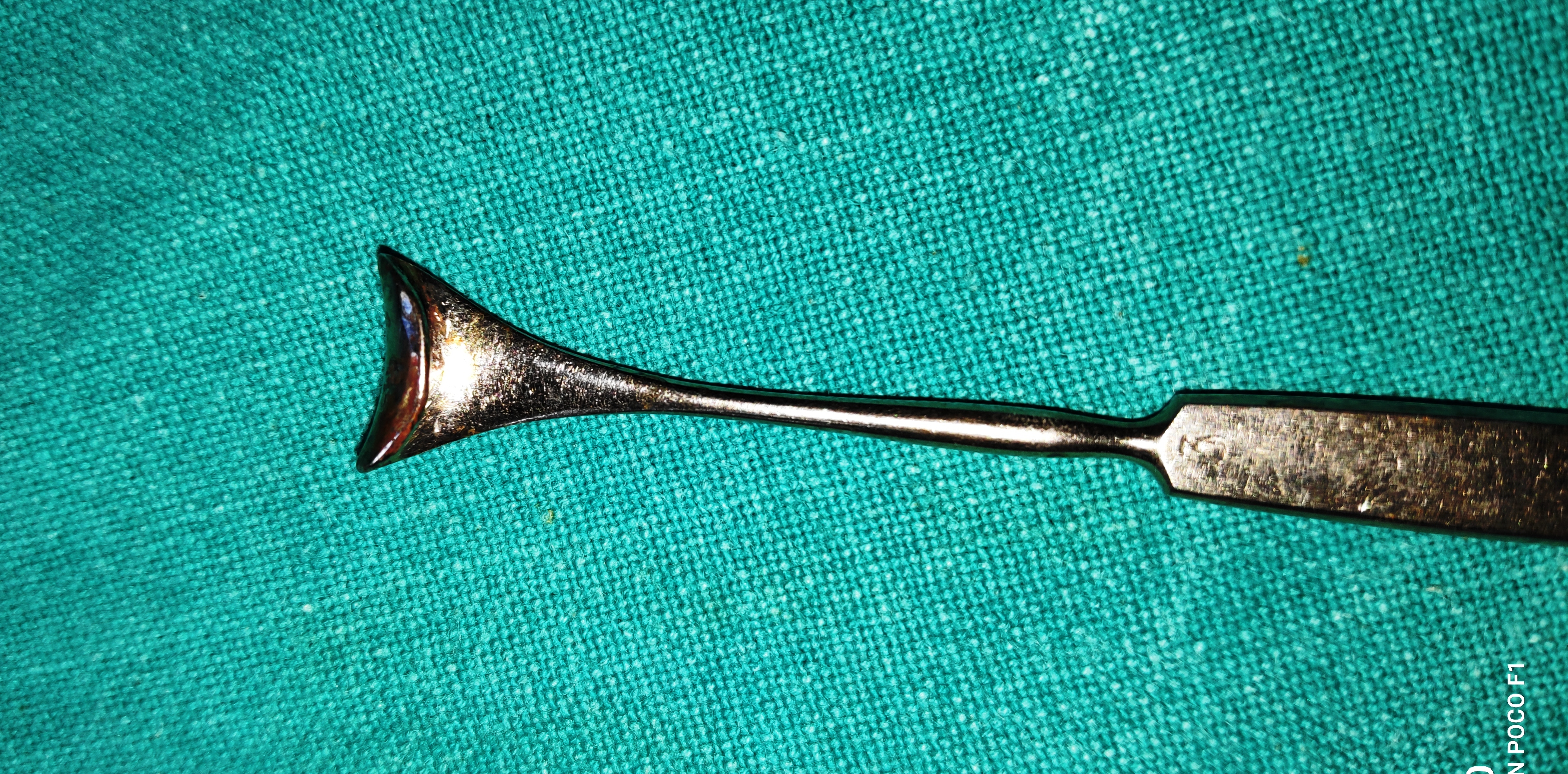
- Desmarres Eyelid Retractor
- It’s a blunt retractor with solid plate style design which has the bent tip. It has a smooth edge and is blunt and atraumatic.
- Uses
- It is used to double eversion the upper eyelid for fornix examination or FB removal.
- Used to retract the skin soft tissue during orbital or eyelid surgeries
- It can be used retract eyelids during sort procedures or for ocular examination in blepharospasm.
- Serrefine Dieffenbach(bulldogclamps)
- Its self-retaining forceps, it has a spring mechanism. On pressure, it opens and once you release the pressure it closes
- Uses
- Used to secure suture and prevent entangling with each other.
- It can keep the eye drapes in place
- Bard-Parker Handle
- It is a long slender handle which can host any type of the blade. The tip of the handle has a peculiar indentation which matches the blade. It is compatible with any blade 11 No., 12 No., 15 No. Etc. The handles are often reusable, with the blades being replaceable.
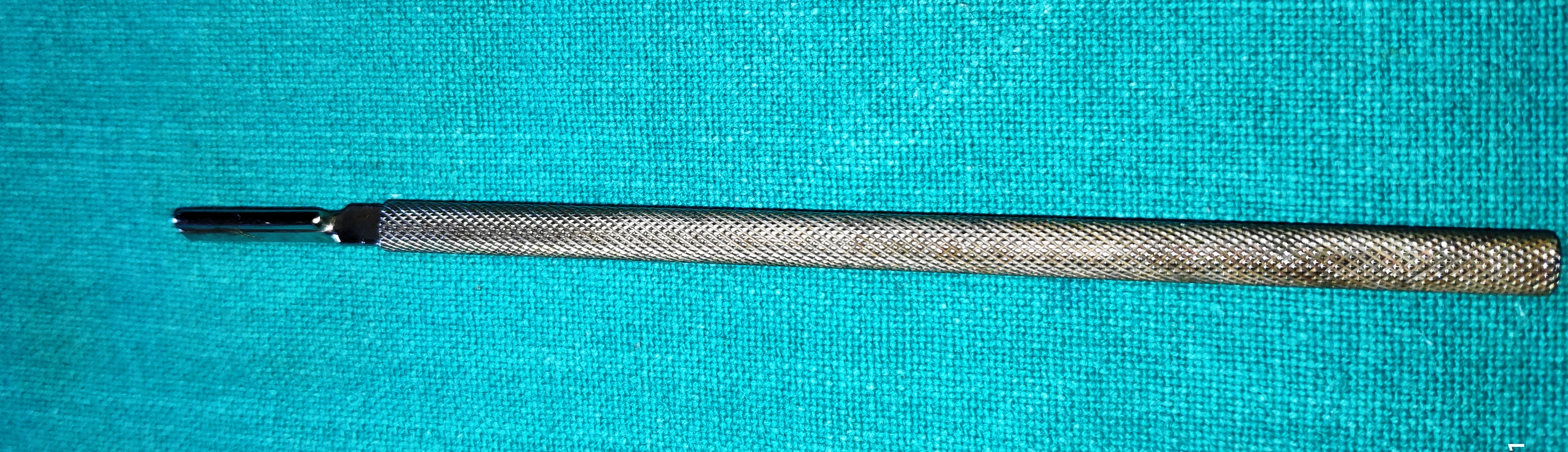
- Frazier’s Surgical Aspiration Tip
- It’s a long hollow tube with corrugation for the rubber pipe and blunt tip. It ranges from various sizes depending on the severity of bleeding. It has a cutoff vent hole controlled by the thumb.
- Uses
- It keeps the surgical field clear, aspirates the blood and blood clot during orbital surgery, DCR etc.
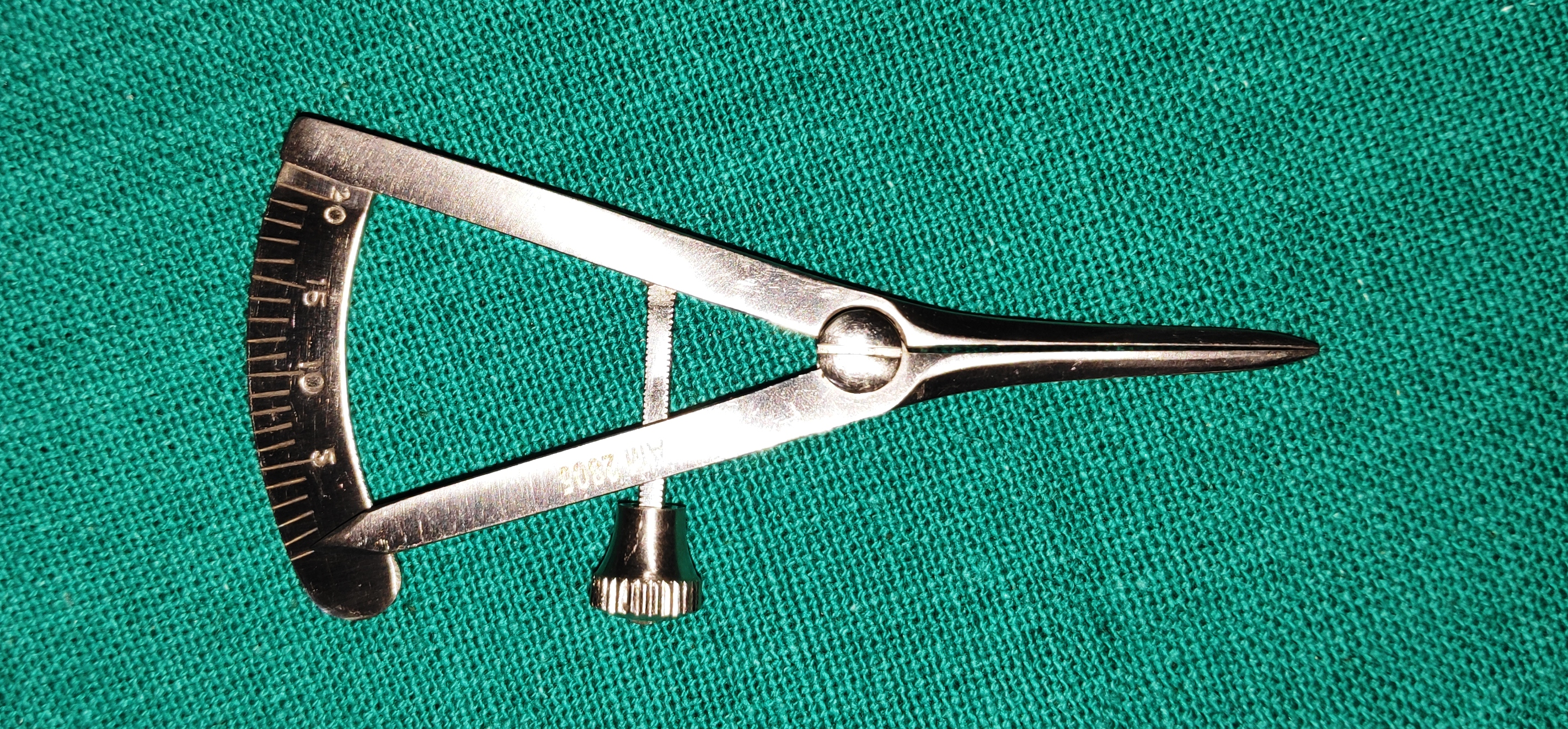
- Castroviejo Calipers
- It has a screw-locking mechanism. With marking 00mm to 20 mm. With 1mm increments.
- Uses
- It’s used to measure lesions/tumour etc
- Used to measure graft or placement of incisions.
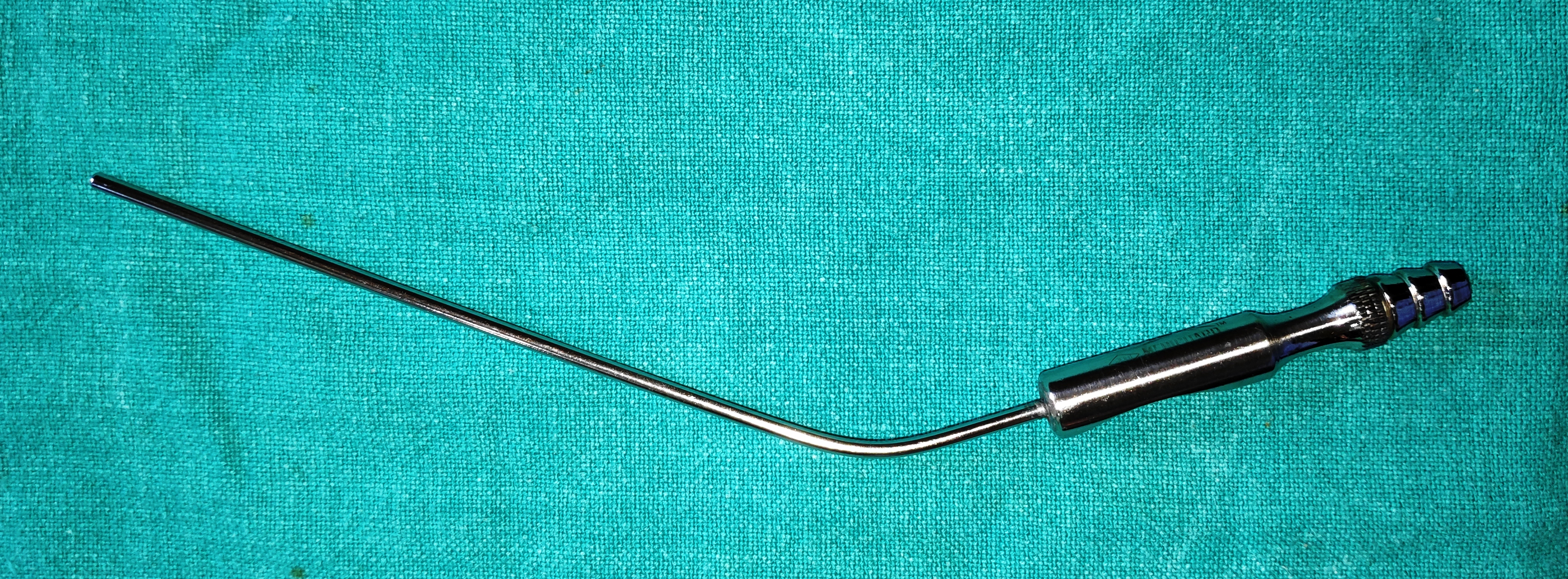
- Traquair Periosteal Elevator
- It is a long slender instrument with 90ᵒ bent at the end. The ends are blunt and atraumatic.
- Uses
- It is used to separate the nasal mucosa from overlying anterior lacrimal crest and lacrimal bone and have a separation plane.
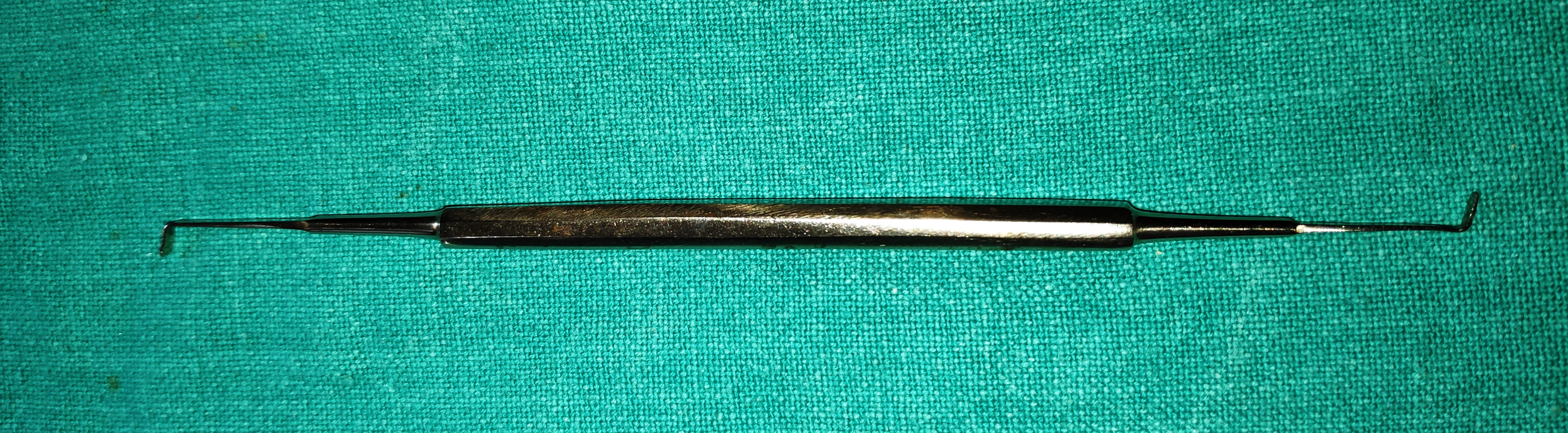
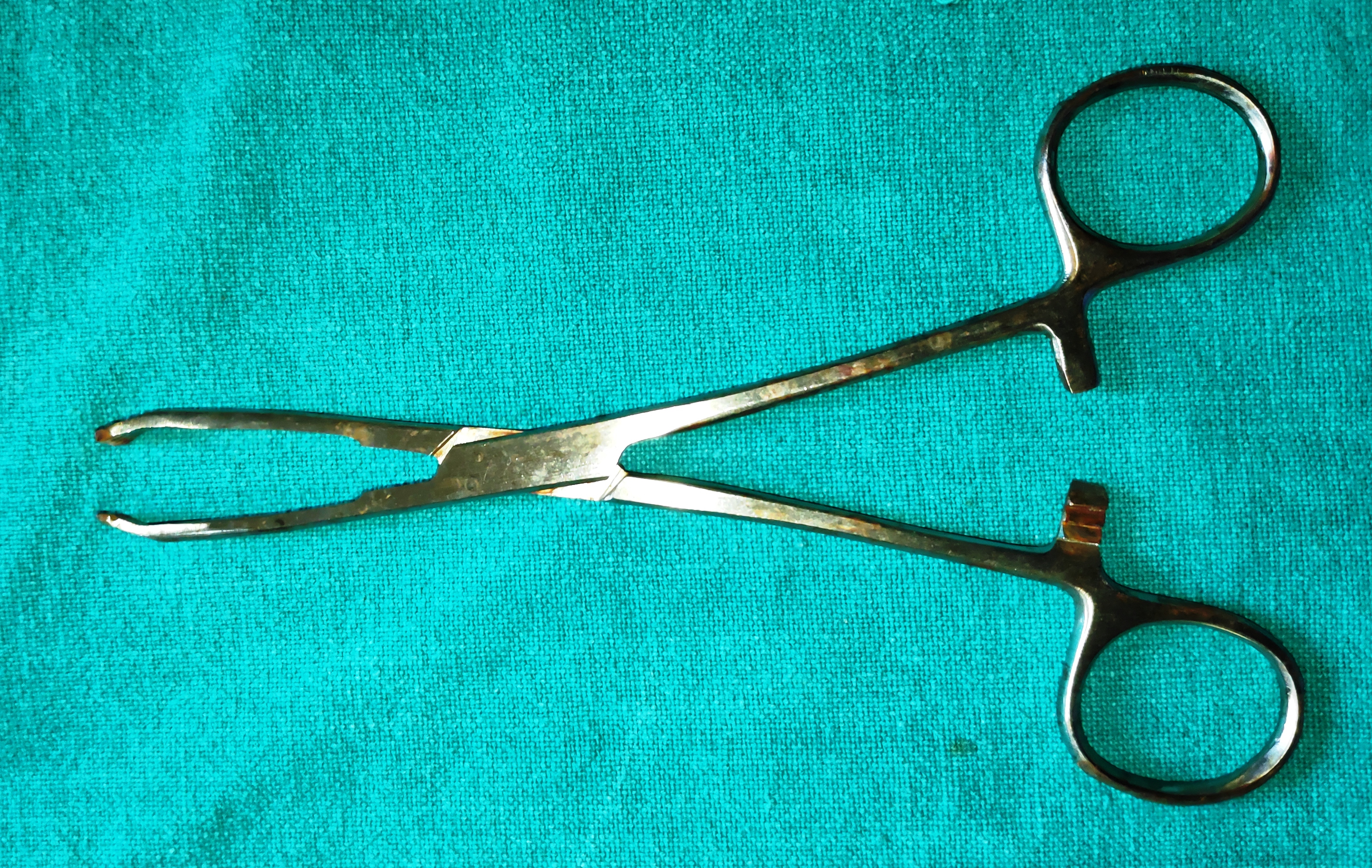
- Allis Forceps
- It is the camp with sharp teeth which provides good holding power.
- Uses
- To hold the lacrimal sac and helps complete removal of the sac in DCT.
- To grasp tumours thereby lifting them and aiding complete removal.
- It is used to hold the tissue and retract it off the surgical field.
- It can be used to clamp bleeders
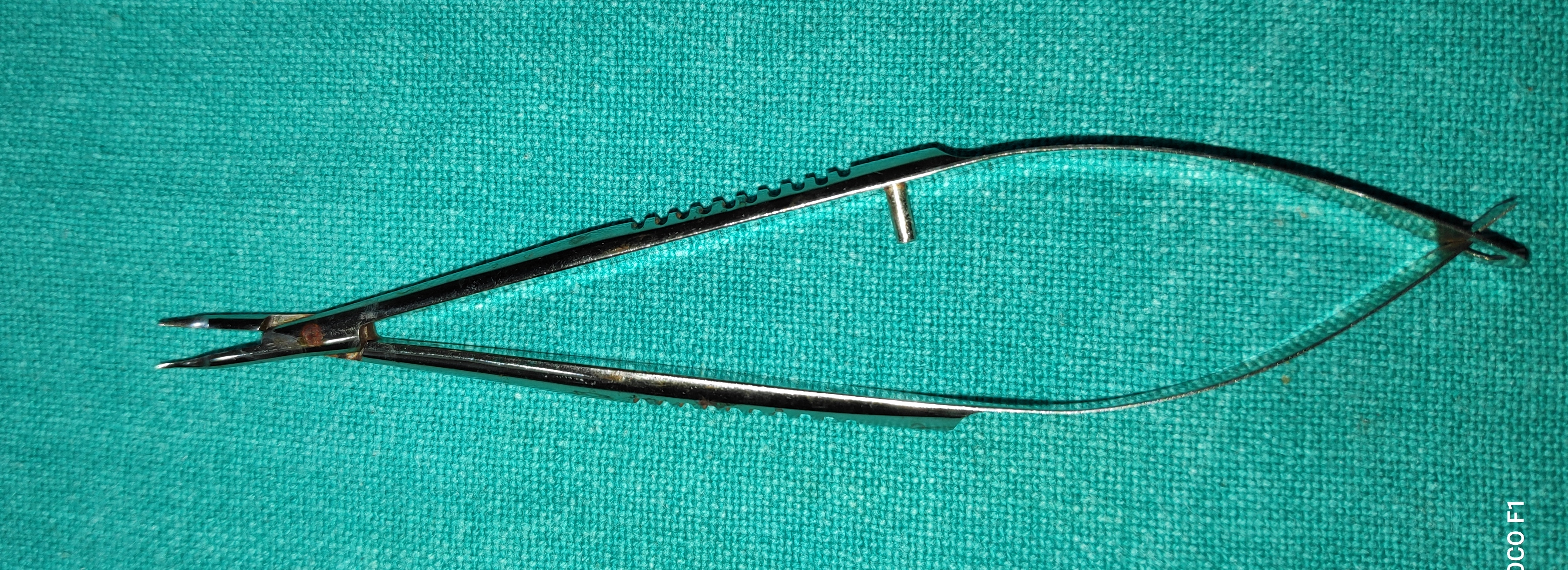
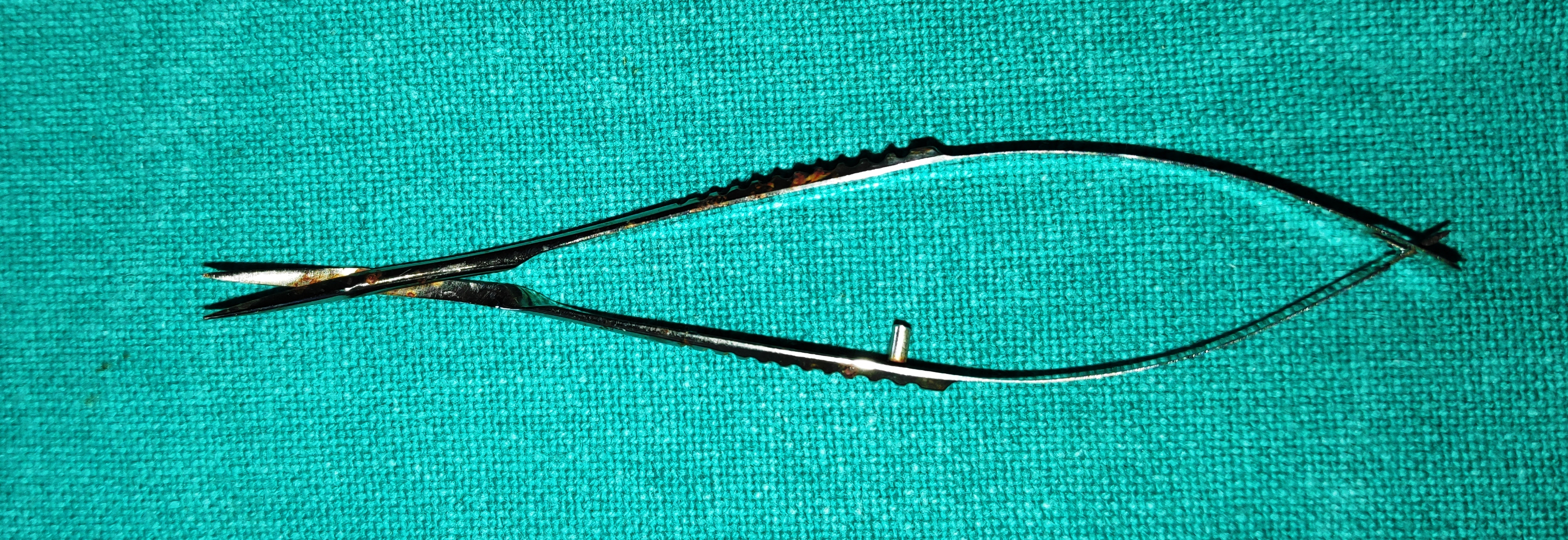
- Vanna's Scissors
- These are very fine, delicate scissors with small cutting blades kept apart by spring action.
- Types- 1) Straight 2) Curved
- Uses
- To cut the anterior capsule of lens in ECCE
- To cut the inner scleral flap in trabeculectomy
- To do papillary sphincterotomy
- To perform iridectomy
- To cut pupillary membranes
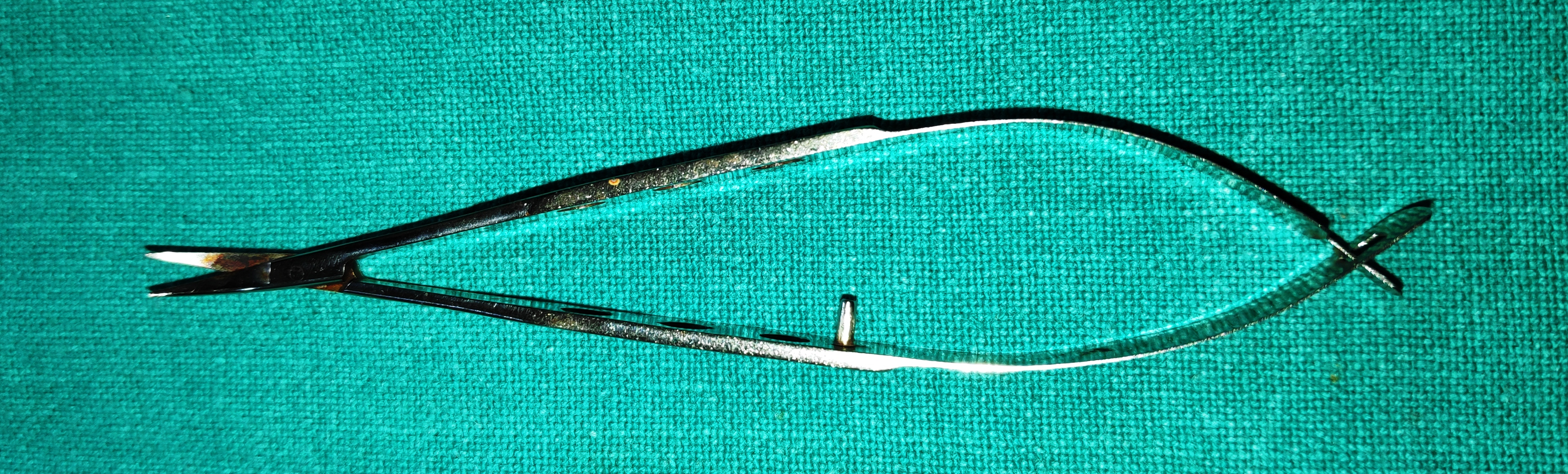
- De Weeker’s Scissors
- They are fine scissors with small blades directed at right angles to the arms. The blades are kept apart giving it a v- shape, by its spring action.
- Uses
- To do Iridectomy
- To do iridotomy
- To perform manual vitrectomy following a posterior capsular tear.
- Corneal Scissors – (Castravejo Scissors)
- They are fine curved scissors. Their cutting blades are kept apart by spring action. They are available in various shapes and sizes. Blades are angulated to facilitate manipulation and are curved to conform to the curve of the limbus.
- The blade which is introduced into the anterior chamber is 1mm longer than the outer blade. The longer blade is rounded in the fashion of a spatula to minimize the trauma to corneal endothelium and iris.
- The second advantage of a longer inner blade is that it does not remove itself from the eye upon each time thereby eliminating the possibility of reintroducing the blade.
- Uses
- To enlarge corneal or corneoscleral incision for cataract and keratoplasty operation
- To cut the scleral or trabecular tissue in trabeculectomy
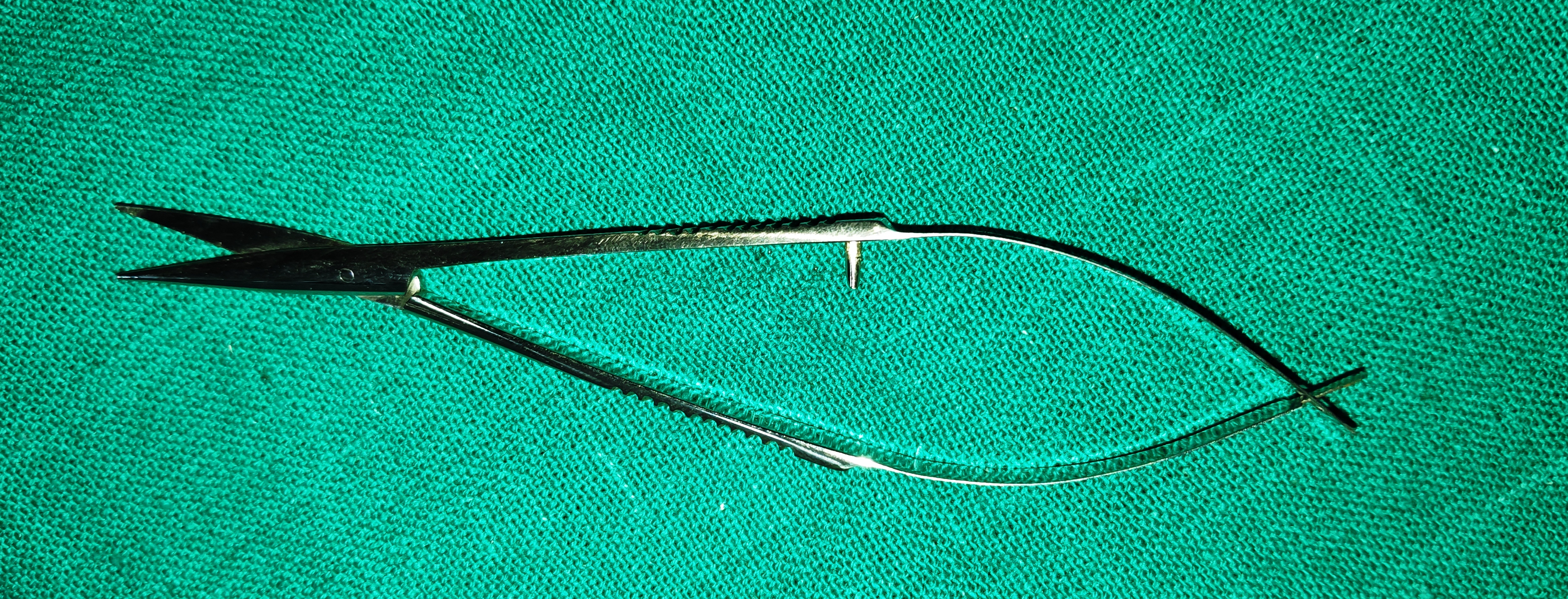
- Westcott’s Scissors
- They are stout scissors available with straight or curved blades with sharp or blunt tips.
- Blades are kept apart by spring action.
- Uses
- For cutting and undermining conjunctiva in various ophthalmic surgeries.
- Can also be used instead of corneal scissors for creating limbal sections.
- Muscle Hook
- It is a long slender rod-like instrument with a 90ᵒ bend tip with a round tip.
- Uses
- It is used to hook the rectus muscle while enucleation.
- It also increases the exposure of the sclera by hooking the rectus muscles while suturing the laceration or to access the retro-orbital structures

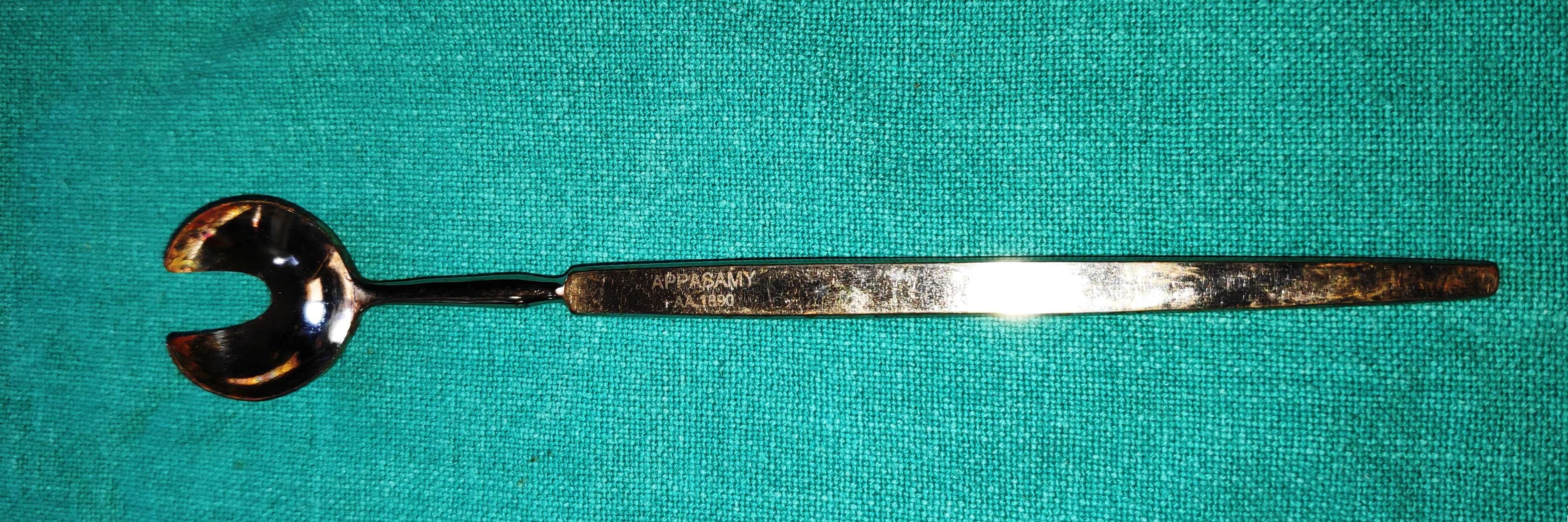
- Wells Enucleation Spoon
- It is a spoon-shaped stout instrument with a groove for the optic nerve to fit in, this also helps to trace and guides the optic nerve for easy identification and cutting.
- Uses
- It is used for enucleation of the eye for intraocular malignancy, for eye harvesting, or for removing the painful blind eye.
- Enucleation Scissors
- It is a long stout slightly curved scissor. It has a blunt tip, the length is essential to reach the optic nerve without damaging the other structures.
- Uses
- It is used to cut the optic nerve while enucleation.
- It can be used for blunt dissection.

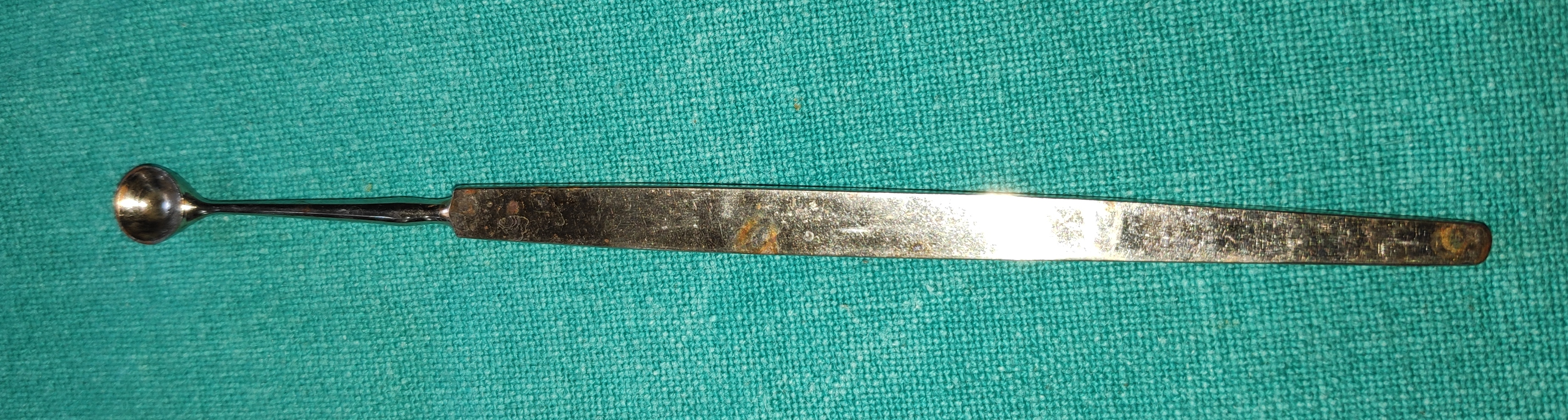
- Bunge Evisceration Scoop
- It is a spoon-shaped instrument it has smooth edges, blunt atraumatic.
- Uses
- It is used to scoop the uveal tissue and intraocular contents during evisceration.
- It can be also used for blunt dissection.

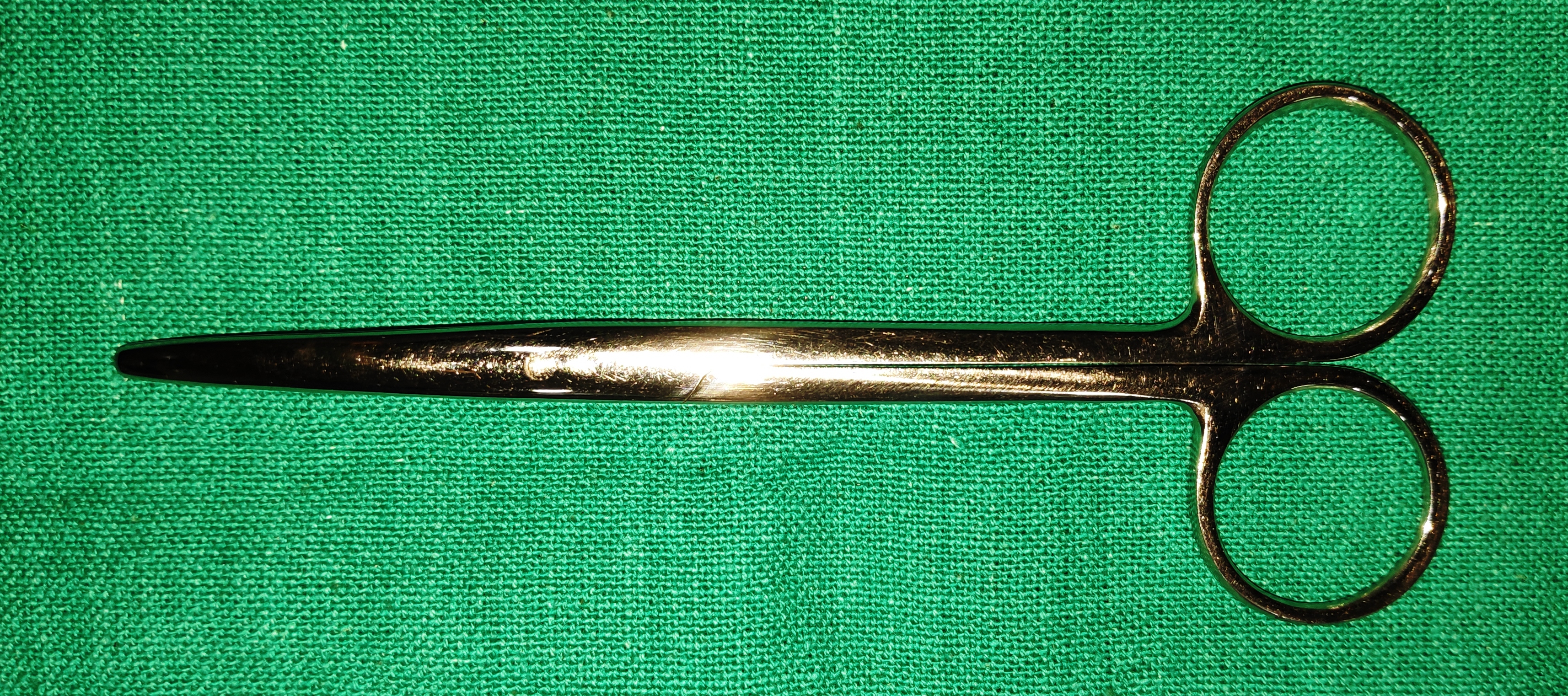
- Needle Holders
- It has the spring action, with a straight blunt tip. The tip could be either straight or curved
-
- Uses
- o It is used to hold the needle for putting sutures.
- o It is used to make the cystitome with the 26-gauge needle tip.
- Uses